Does your router struggle when it comes to extending WiFi outside your house? Whether you want to expand the connectivity to your garage, backyard, or even another building a few feet away, you’ve come to the right place.
Below are the five ways you can extend the WiFi range outside:
- Using a WiFi Range Extender
- Establishing a Wireless Bridge
- Setting Up an Access Point
- Building a Mesh Network
- Running an Ethernet Connection
Without further ado, let’s get in.
How To Extend WiFi Range Outside?
In the coming sections, you'll get to learn about each of the above-mentioned methods, along with their fundamentals, functionality, effectiveness, cost, and Pros & Cons.
1. Using WiFi Extender
WiFi extenders are quite popular networking devices that let you extend the range wirelessly. It's basically a compact device that can be placed between a router and a WiFi dead zone.
Extenders connect with your wireless router and repeat signals from it. And since it does wirelessly with a simple concept, it's obvious that you’re going to receive 1/4 of the speed of your router/connection.
The signal quality, however, is good in general, and you can expect it to enhance the wireless coverage by 1,000 Sq Ft to up to 3,000 Sq Ft, depending on the model you pick. For more details, check my thoughts on how far extenders reach.
Note: Some manufacturers also call them “WiFi Boosters” and “Repeaters”.
How Does It Work?
The functionality of a WiFi range extender is fairly simple. All you need to do is select the place to put a WiFi extender, plug it in the nearest power outlet and set it up with your network. Luckily, most extenders can be set up using a companion app.
Once configured, you're done. As soon as you move to this area, your devices will connect to the extender's network.
Benefits & Drawbacks of a WiFi Extender
Pros
- Repeats signal to distances
- Cost-effective solution
- Easy to install & set up
- Mobile app support
- Handles basic tasks
Cons
- Noticeable speed drops
2. Using Wireless Bridge
A wireless bridge involves a set of devices that lets you connect two or more networks or network segments over a wireless channel, sort of like a bridge.
It is used to interconnect networks between two buildings in close proximity, in manufacturing and shipping sites, offices across a street, and so on.
How Does It Work?
These use radio signals in optic/laser or microwave links to interconnect two access points. A “wireless bridge” device uses unidirectional antennae to send and receive signals, alongside connecting with internet plans on the other side.
In this manner, it provides an option to connect two IPs through a wireless link. The signals through wireless bridges are further sent to the devices using Ethernet cables, providing opportunities for more connections over a large area.
Benefits & Drawbacks of a Wireless Bridge:
Pros
- Traffic is substantially reduced
- You can connect two IPs at once
- It connects different architecture
- It acts as a repeater to take your signals farther away
- It extended the physical network
- Bridges increase the number of network segments and attached workstations
Cons
- Slower than repeaters
- More expensive than repeaters
- Bridges don’t filter broadcasts
- Complex network topology
- Doesn’t scale to a too large network
3. Using Access Point
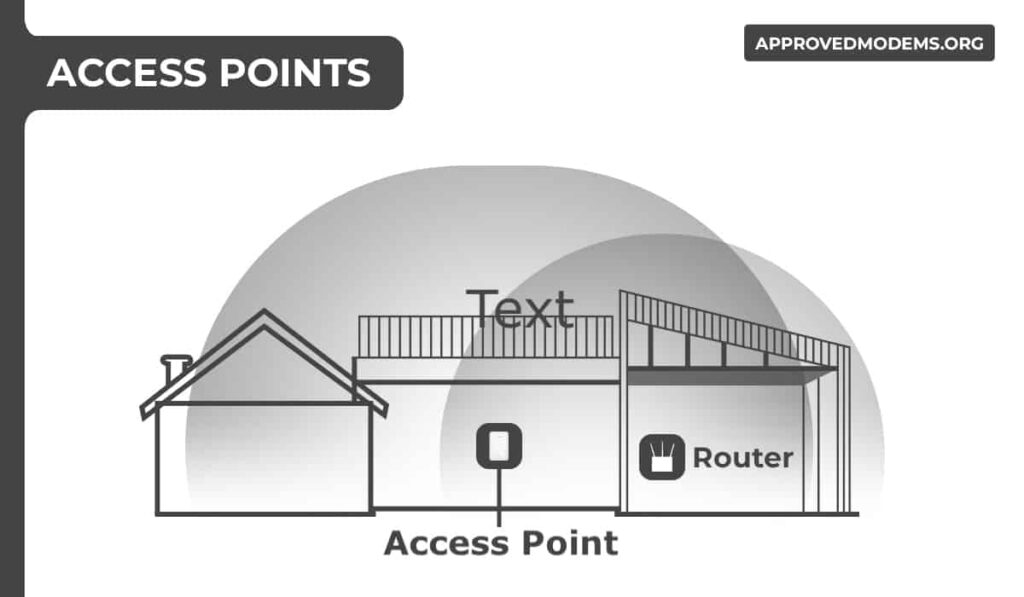
If you are struggling with the WiFi, you must have come across the term “wireless access point” many times.
You can add them to your current network for improved wireless coverage, and it’s getting more common to install multiple of these to expand the signals throughout a large property.
How does it work? Access points are connected directly to the router or network switch through a data or Ethernet cable, which gets it the required connection and bandwidth.
The signals are transmitted to the devices through a 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz frequency band. You can now access the internet in unreachable areas like in your yard or garage.
Benefits & Drawbacks of Access Point:
Pros
- Good for upstairs or outdoors
- Strong internet even with multiple users
- Multiple Access point connection
- Flexible networking
Cons
- High cost
- Not suitable for individual use
- Poor stability
4. Using a Mesh WiFi
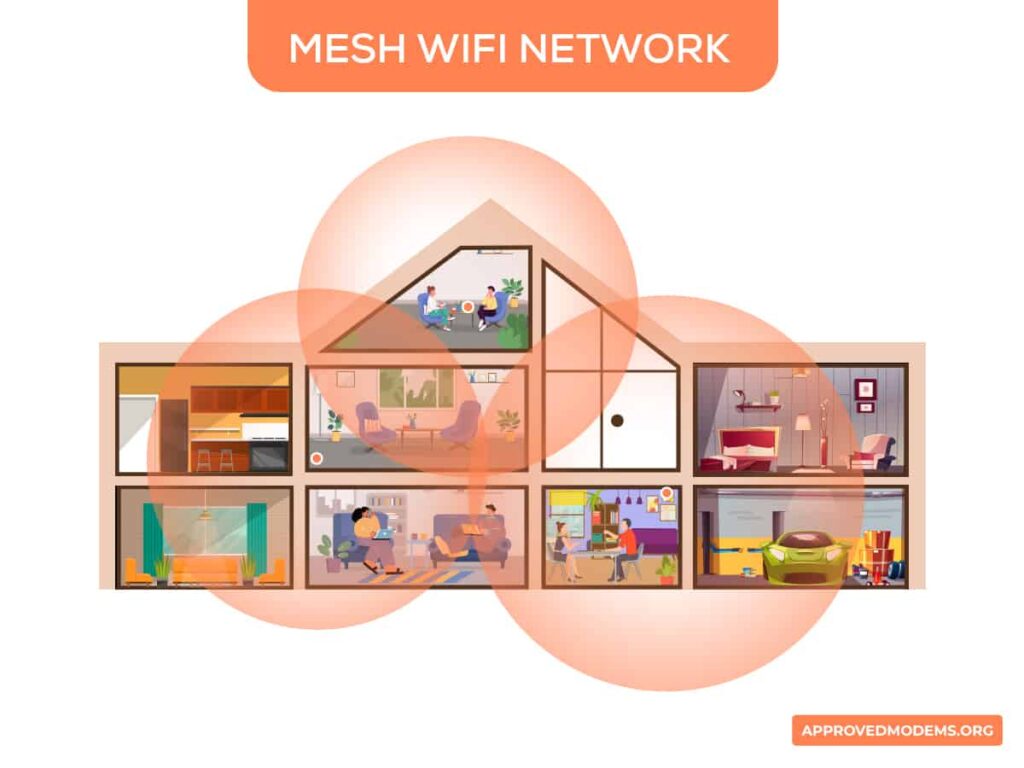
A mesh system works just by creating a mesh network by connecting with WAP (wireless access points) nodes installed in different parts of your house.
The networking infrastructure is simplified and decentralized as a node has to send signals to another node and transmit them to the connected devices.
To explain how a mesh system works, let me first tell you its components, i.e., a main hub, mesh nodes, and clients.
Here the main hub connects to the modem or gateway to access the required bandwidth and transmits to the WAP devices or mesh nodes that act as satellites, which are further accessed by clients.
The nodes can be more than one, depending on the area you wish to cover. This way, a robust and unassailable mesh network is created over a large area at a stretch.
👉 Suggested Read: WiFi Mesh vs Extender
Benefits & Drawbacks of Mesh WiFi Network:
Pros
- Ideal for large homes and areas
- Seamless connectivity
- Easier setup than access points
- Much more secure & scalable
- Much present networking equipment can be converted into main hubs or nodes
Cons
- They're expensive
5. Using Ethernet or Powerline
Powerline adapters are the last, most inexpensive, yet reliable option for extending WiFi to outbuildings or farther distances.
In this, you have two adapters, one connects to the router, and the other stays closer to the devices staying connected to the first adapter, both using an ethernet cable.
So, the signals or bandwidth is passed on from one adapter to another, and further to your available devices.
Benefits & Drawbacks of Ethernet or Powerline:
Pros
- Much cheaper than other options
- Uninterrupted and lag-free connection
- Can connect to multiple devices at once
- Ideal for high-bandwidth tasks
Cons
- Can be affected by electrical interference
- Requires a large ethernet or MoCA cable
- Limited configuration options
TL;DR [Key Takeaways]
Now that you have finished reading through the options, here are the key takeaways:
- The simplest and most effective option to extend your signals outdoors is using a mesh system with additional satellite units. But it comes at an exorbitant cost.
- In theory, an outdoor extender would be the best option, but there aren’t many consumer-grade extenders available.
- If you have a large office or a building to cover, setting up access points would be a viable option.
- Powerline adapters are only for people with limited budgets and have options to pass ethernet cables through walls.
Related Read: How to extend WiFi to the detached garage?
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, there are certain devices like bridges, repeaters, and mesh networks that extend your network far away to the outskirts.
One of the simplest ways to extend your wireless network 400 feet away is using a WiFi extender. Or if you have much to spend, you can invest in a mesh system.
As far as my tests go, the best standalone extender in terms of its ability can extend up to 3,000 Sq Ft, which means your yard and garage should be filled with powerful signals.
Access point actually does a better job than extenders in terms of signals it transmits, and should get you better speeds over your connected devices.
Outdoor extenders are a bit different from traditional ones as they are specially designed to endure harsh weather conditions like rain, wind, and others. Besides, they can deliver much better and stronger signals to far-off places. These features make the extenders worth the price they come at.





