Do Routers and Modems Affect the Internet Speed?

Yes, the modem and router you use can affect your internet speed.
But how?
Well, these networking devices direct traffic between the ISP and the devices in your house. Now, how this traffic is handled eventually determines your internet speed. Imagine being stuck on a jammed highway, making your car go slower.
From the router’s hardware, wireless standard, channel bonding on your modem, type of house (obstructions), router’s placement, number of connected devices, etc., anything and everything can affect your speed.
Throughout this article, I shall discuss several such factors and suggest optimal configurations to get the most out of your internet connection. So let’s begin!
How Routers Affect the Internet Speed
Routers work like bridges between the internet and the home network. While the modem connects directly to the ISP, the router routes the data packets modulated-demodulated by the former.
The routing process involves passing the data packets to smartphones, computers, and other devices. Below are the factors that can affect the Internet:
- Processing Power: A wireless router is responsible for routing and switching data packets. Suppose the internal components are subpar, and there is less processing power in play. In that case, it might take the device more time to decide the paths for routing and switching, eventually slowing down the speed.
- Wireless Standard: Routers support different standards, like the 802.11ac, 802.11n, and more. Newer standards like 802.11ax or Wi-Fi 6/6E offer the best speeds due to less congestion and the availability of more non-overlapping 5 GHz channels.
- Frequency Bands: You cannot expect insanely high speeds if you are on the 2.4 GHz band, the one with a higher range. Similarly, the 5 GHz band also has its limitations. It can offer the best speeds, but the WiFi range is limited. For example, if you have the router downstairs and you wish to access the internet on the terrace, the 2.4 GHz band with lesser speed limits will come to your rescue.
- QoS (Quality of Service): Most routers these days come with QoS. Activating it can help speed up specific tasks like games, video calls, and more. Without QoS, task-specific speeds can be on the lower side.
- Connected devices: Your internet connection might take a hit if there are multiple devices are connected. Each device will each into the bandwidth and can lower throughput. For example, if your router supports 50+ devices, you should not connect more than ten across bands to best use the speed limits.
- Security Controls: Having the security settings properly configured can help with the speeds. Your connection quality might suffer if the router’s security standards aren’t clearly defined.
- Firmware: Like any other network device, even routers need to be checked for firmware updates. Not installing these updates regularly can hinder optimization and slow down internet speeds.
- Router Placement: And finally, where your router is placed has a lot to do with the internet speed. If thick walls and even big electronic appliances are in the line of sight, the speeds can go down. Find the best place to put a router.
How can a Cable Modem Affect your Internet Speed?
As mentioned earlier, like routers, even modems have a role to play when it comes to internet speeds.
Firstly, modems act as gateways between the ISPs and the networks. This means they convert the analog streams from the ISP to the digital form — the form your network understands. And just so you know, routers take the digital streams and move them to other devices.
Based on how modems work, here are the factors that can impact the speed:
- Modem Technology: There are different kinds of modems around — Cable, DSL, and even Fiber Optic. Fiber gateways are the fastest ones around. While the DSL modems can automatically restrict your speed-specific abilities.
- Compatibility: Not every modem tech is compatible with every ISP. For example, if you prefer a DSL connection, CenturyLink is the option to go with. COX, Xfinity, and other options are around for cable modems.
- Data Rate: Modems boast preset transfer rates for data. In case that is lower than the ISP’s plan, you are bound to experience slowness. For example, say your Modem’s data transfer speed is 50 Mbps. That way, it will only be able to push through 50 Mbps instead of, say, a 100 Mbps plan offered by the provider.
- SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio): Here is a technical element that ascertains the quality of the connection established between the modem and the coaxial cable or any other cable. A low SNR can lead to lower speeds and also data loss.
- Cable Connections and Quality: If you have a top-rated modem, but your internet speeds are lower than usual, you might need to look for broken or even loose cables.
- Firmware or Software: Like the router, you should regularly update the modem firmware to ensure optimal performance. Dated firmware is a speed killer.
- Error Correction: Modems come with built-in error correction support for data integrity. However, excessive line noise, poor cabling, cross-talk, impulse noise or power spike, and signal attenuation can lead to multiple errors. Frequent correction then slows down the speeds.
- Heat Dissipation: Overheating can be a reason for speed throttling. Modems that do not have decent ventilation are expected to slow down the internet throughput, eventually leading to hardware malfunction.
Other things that Affect the Internet Speed
Besides modem and router-specific bottlenecks, here are a few elements that could impact your internet speed:
- Malware affecting devices
- Network congestion
- Background apps causing interference
- Internet providers throttling the speeds
What is a Good Internet Speed?
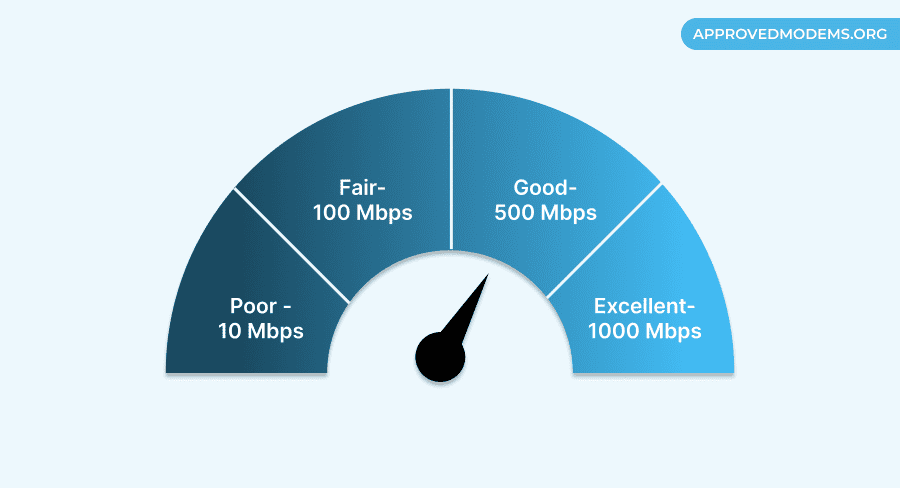
A good internet speed is a figure that works best for you. For instance, if you have multiple laptops, IoT devices, phones, and other devices to connect to — something to the tune of 500 Mbps could be a decent number.
For standard HD streaming on one device at a time, video conferencing, and other specific needs, anything in the 50 Mbps to 100 Mbps range is sufficient. For basic browsing and similar tasks, anything close to 25 Mbps works.
It’s recommended to use an interactive quiz calculator to determine what internet speed you need based on the number of users and usage type.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will a new modem make my internet faster?
A new modem might make the internet fast if it brings in new technologies and works with a compatible ISP. Plus, you need to see that it is properly ventilated and has a high Signal-to-Noise ratio.
Can a modem slow down internet speed?
Yes, if the modem experiences too much heat or is paired with an incompatible ISP, it might lead to serious speed-based issues.
Should my router be faster than my modem?
A router usually is rated faster than the modem as while the modem works directly with the ISP’s offering; the router is meant to connect to the network. Therefore, the router often has speed thresholds over 3 Gbps, near and far band included. For optimal performance, the router should have the highest possible speeds for each band to be able to handle data from the modem.
What is limiting my internet speed?
Anything from ISP limitations to the number of devices connected to the network to massive network congestion might limit your internet speed.
Conclusion
Both routers and modems are necessary for good internet speeds. However, a modem is more important regarding utility; if you have a handful of devices at home and do not seek wireless connectivity, you can only use the modem.
However, a good router is essential if you have a sizable home and more-than-basic connectivity needs.
You can even consider investing in a 2-in-1 modem router combo that works as both modem and router to minimize the need for research and lower the chances of speed drops due to individual bottlenecks.
