Internet Bandwidth vs Speed: What Are The Differences?

Are you on the fastest internet plan but your WiFi is only picking up half or even 1/4th of the speed? That’s because of the difference in the Internet bandwidth and speed.
A high bandwidth doesn’t necessarily mean good downloads and uploads. Confused? Read through this simplified yet detailed comparison between Internet bandwidth and speed and enlighten yourself with these networking elements.
Key Difference: Bandwidth is how much data can be downloaded and uploaded from or to your device. Whereas speed is how fast it can be done.
Internet Bandwidth vs Speed
In the following sub-sections, I shall explain both, along with the difference and example. So, let’s get started without any further ado!
What is Bandwidth in WiFi?
Bandwidth is a networking term defined as the maximum amount of data transmitted over a channel in a particular time.
To explain it in simple terms, look at the picture above and think of bandwidth as a highway, where the vehicles (data) are moving at a similar speed. And to accommodate more vehicles, the highway must be broader.
👉 Related reading: How To Cancel Cox Services
What is Speed?
Speed refers to how fast data is moving through the channel, while bandwidth is the frequency of the carrier channel.
Speed on the other hand refers to how fast vehicles (data) are moving on the highway. It is measured in “Mbps or megabits per second”, and the higher the number is, the speedier your online activity will be.
However, if you’re not sure about your requirements, here’s a tool to help you decide the internet speed you need. All you gotta do is play a simple quiz & get accurate recommendations!
How Does Bandwidth Affect Speed?
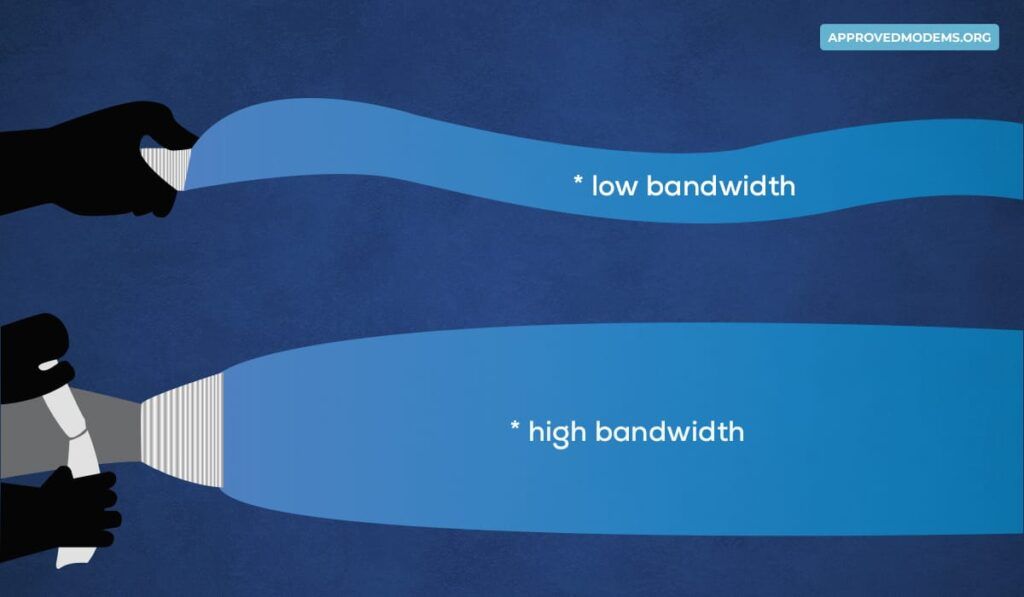
Bandwidth has a proportional impact on the speed, i.e., the greater the bandwidth, the better the speed, and vice versa.
Here’s how bandwidth work:
If you have a slender pipeline, a lesser quantity of water can flow, irrespective of how fast the flow is. In networking terms, less data passes through the channel at a time, thereby decrease in speed.
But here’s an anomaly. If you’re subscribed to a Gigabit plan, that’s the bandwidth, and the speeds won’t necessarily be equivalent. This is because the channel is capable of transmitting Gigabits of data, but that doesn’t mean each of them travels at the same rate, which further decides your speed.
Greater the number of connected devices, time of day, and other factors also decide the rate at which data is passing through the channel.
Note: Your internet equipment also affects the output. This is why I suggest getting a modem and router that supports your subscribed internet speed plan.
Recommended Resources:
How To Know Your Internet Speed and Bandwidth?
- Contact your ISP (Internet service provider) to know your current bandwidth or the plan you’re subscribed to.
- Multiple tools like Capsa, PRTG, Network Analyzer, and others deliver detailed insight into bandwidth usage.
- Many routers have built-in bandwidth tools that let you see how much bandwidth is consumed by your network. You can find these in router settings, accessed by putting in your IP address into the web browser.
- Using speed testing tools like Ookla, Speedtest.net, and others provides an estimate of your bandwidth.
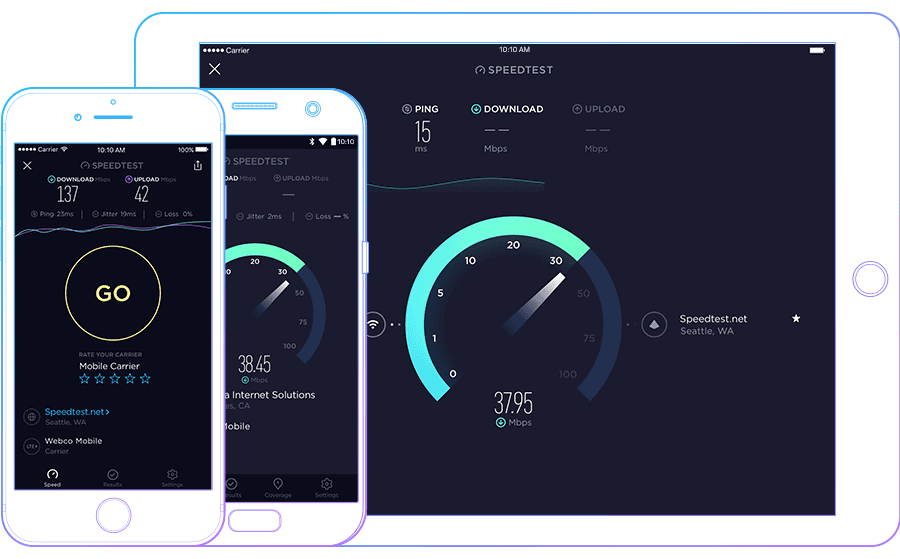
Checking the speeds isn’t stressful, and you must carry on the following steps:
- You can connect your devices through WiFi, but I’d recommend using an Ethernet cable for the most accurate results.
- Disconnect any other devices that might be connected and close any internet browsers or programs running on your computer.
- Then, visit websites like “Ookla, speedtest.net, and others” and click on the go. It analyzes your network and displays your download and upload speed.
- If the speed seems very less, contact your ISP or restart your router and check again.
👉 Related reading: How To Cancel WOW Internet Services
Examples of Bandwidth
Frequently Asked Questions
Is bandwidth the same as speed?
No, bandwidth is the maximum data your connection can handle, measured in megabits, while speeds are measured as how fast data travels, measured in megabytes per second.
Does increasing internet speed increase bandwidth?
It’s actually the opposite. If you’re subscribed to a 2 Gbps connection, the speeds don’t get higher than that. But speeds on a 2 Gbps connection are more than in a 1 Gbps one.
Is more bandwidth better?
Yes, more bandwidth allows for faster data transfer rates and smoother streaming u0026 internet browsing experiences. However, factors like network congestion, more available devices, and distance from the source affect the speed, and increasing the bandwidth won’t necessarily improve the performance.
What type of internet has more bandwidth?
Fiber-optic internet, which uses fiber-optic cables to transmit data, can provide very high bandwidths of up to 1 Gbps or more, making it one of the fastest types of internet available.
Conclusion
Your speeds are bound to be less than your bandwidth, but if values are much inferior, you should access the conditions and contact your service provider.
As you’ve gone through the Internet Speed vs Bandwidth comparison, I’d also suggest you learn the differences between throughput and latency.
Continue reading:
