Latency vs Throughput: How They Affect Each Other?

Latency and Throughput are two key metrics used to measure your network performance. Latency means the time taken for data to reach the destination. While throughput in networking refers to the amount of data being transferred.
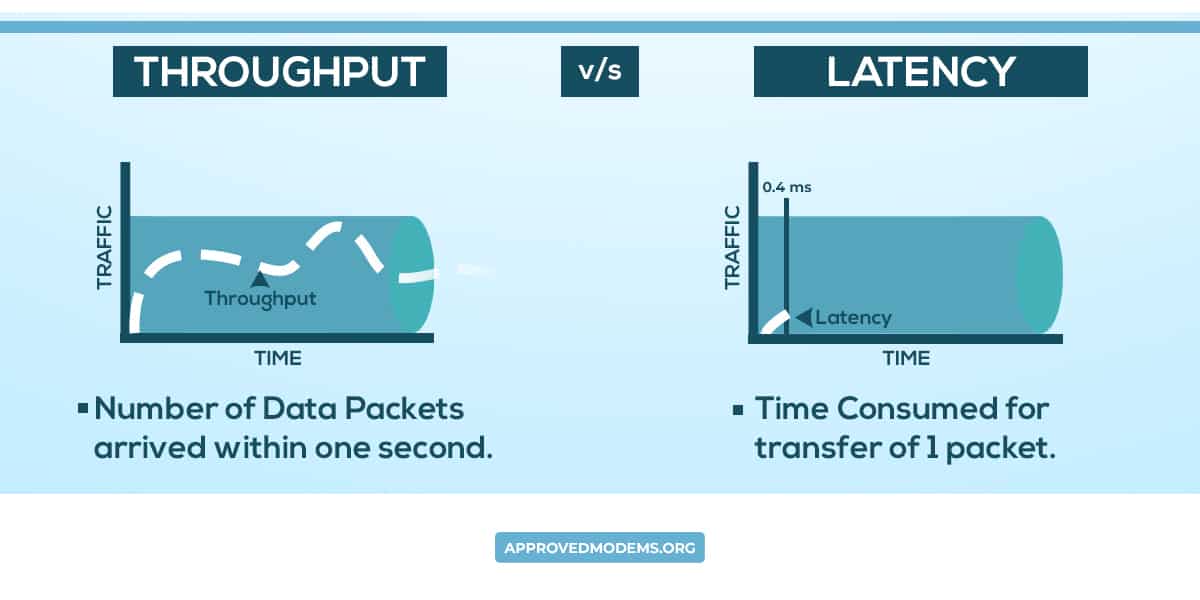
In layman’s terms, imagine water flowing out of a foot-long pipe. Latency is the time it takes for the water to travel the foot-long pipe, and throughput is the amount of water flowing out. That’s the basic difference between latency and throughput.
Understanding the factors affecting them will allow you to get rid of the sticking points and get the most out of your internet. In this article, I shall compare throughput vs latency and explain how they relate to each other and what can be done to improve.
Latency vs Throughput: Differences & Relationship
Higher latency can affect your internet throughput, which reflects on the bandwidth and performance. Lower throughput can cause higher latency, resulting in a poor network.
For a network to perform well, you’ll need a high-bandwidth device with high internet throughput and low latency.
Bandwidth in networking refers to the total or maximum speed capacity. It refers either to a networking device (WiFi router) or the network and the volume of data it can transmit at any instant. Like throughput, it is measured in Kb/s, Mb/s, Gb/s & so on.
Hence, latency, throughput, and bandwidth relationships are interconnected.
While a higher bandwidth enables higher throughput and lower latency, it doesn’t guarantee either. The throughput is contingent on your internet package, and the latency depends on the quality of your network connection. Similarly, higher bandwidth doesn’t necessarily mean higher speed.
What Causes Low Throughput & How To Improve It?
In this section, I’ll take you through the major causes of low throughput and the solutions to improve your network performance.
1. Hardware Performance
More often than not, the hardware is the reason behind the low throughput. A mismatch in the hardware capacity, an outdated router, or a bad cable modem can lead to throughput-related issues. Defects in devices more often result in shoddy throughput performance.
List of High-Performance Modems for Different ISPs:
List of High-Performance Routers for Different ISPs:
2. Signal-To-Noise Ratio & Interference
The electromagnetic spectrum is shared with other devices. This makes the wireless network vulnerable to interference, leading to a high noise-to-signal ratio and interference from other Bluetooth, radio-based devices, and neighboring wireless networks. Affecting the internet throughput.
3. Peak Time Traffic
During peak usage hours, the network traffic is prone to be on the higher end. In an instance where the network bandwidth is shared with other end users, the traffic leads to higher packet loss and lower throughputs.
4. RB Utilization
Resource Block allocation and utilization come into play when multiple devices share a wireless network. Higher the number of devices, the higher the load on the network, affecting the RB utilization ratio, and leading to a lower throughput for the devices.
Tips To Improve Network Throughput:
A combination of these solutions mentioned here would help you improve the internet throughput
– Use the latest firmware for devices
– Eliminate Bottlenecks by getting devices with matching specifications
– Configure QoS for prioritizing throughput for devices
– Use a Wired Connection
– Adjust the Router’s Location
– Experiment with MTU
– Upgrade to a router with higher bandwidth
What Causes High Latency & How To Reduce It?
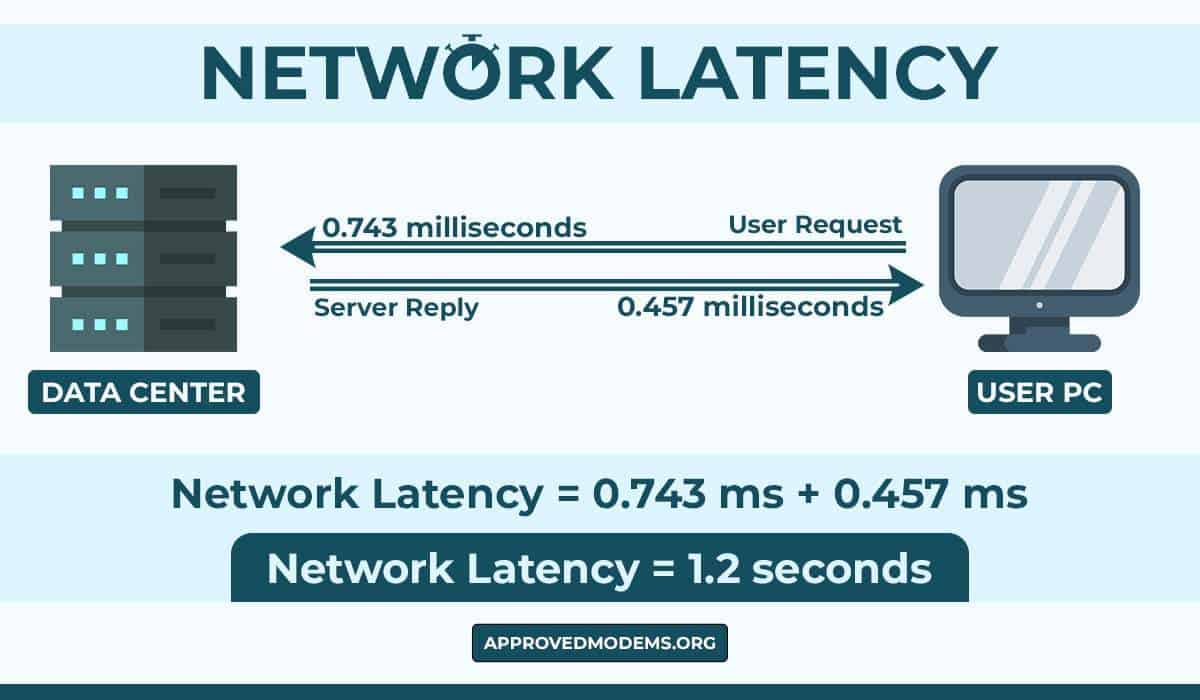
Latency in networking refers to the time delay. High latency means there is trouble with your network performance. There are multiple reasons leading to a higher delay in data transmission. In this section, we’ll go through the leading causes.
1. Distance
Longer the distance between the endpoints, the higher the latency. This is one reason hardcore gamers prefer switching to local gaming servers or the nearest ones for a seamless online gaming experience. They also prefer a 5 GHz band over 2.4 GHz when playing on wireless networks.
2. Transmission Medium
The internet you use plays a role in latency. For instance, DSL, Coaxial, and Fiber rely on wired connections. Unless there is any physical damage, the latency is minimal. But when you compare cable with satellite internet, the latency is high since the medium is air, which is prone to interference.
On the other hand, Fiber optic internet is known for low latency, followed by coaxial cables and then DSL broadband lines.
3. Low Memory
The higher the capacity to store, process and transmit the data, the lower the latency and vice-versa. Lower memory in the modem, routers, and servers makes your network vulnerable to higher latency.
4. Router Speed and Condition
The condition of your router, and its capacity, plays a role in latency. If your router’s specification doesn’t match your internet connection, you will likely face high communication latency.
Note: Megabits and Megabytes are different from each other. Check out my megabit vs megabyte comparison to learn more.
5. Storage Network
The speed at which data is retrieved, processed, and transmitted depends on the storage drives. The faster it can access the data, the lower the latency. It takes longer for the data to be accessed from the storage, and the higher the delay.
6. Delay in Propagation
Any delays in transmitting the signals within the communicating devices would lead to higher latency in transmission.
Tips To Reduce Latency For Better Network Performance:
While some causes don’t fall under the end user’s purview, the action points mentioned below will allow you to mitigate most of the causes for higher latency.
– Use CDN to reduce the distance to the servers
– Optimize the routing
– Use wired connections wherever possible
– Update firmware on routers
– Upgrade to the router with better memory and hardware capacity
Latency vs Throughput Calculator
You don’t need a throughput and latency formula to calculate and measure them, as the internet is loaded with a plethora of free and paid tools.
Let’s see how to measure the latency in network communication with a command prompt. Hence, I will introduce you to the “Ping”. A simple ping-t command to the google.com server will give you information on the quality of your internet connection.
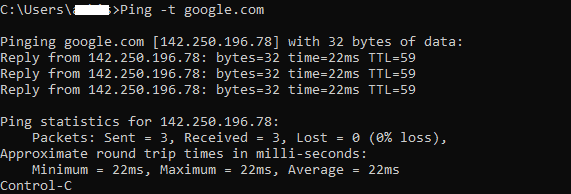
On the command ping -t google.com, your computer sends packets of data to the local google.com server. In case of a successful connection, the google.com server retorts with data packets.
The approximate time taken for the round-trip shown in milliseconds, shown as an average of multiple attempts, is what you are looking for “latency”. The loss percentage shows the quality of the connection between these two points.
The throughput is calculated by sending a file over the network. With the time taken for complete transfer and the file’s total size, you can calculate the amount of data transferred in a second, which is your throughput measure. It’ll either be in Kb/s or Mb/s or Gb/s, depending on your network capacity.
A simple visit to speedtest.net or fast.com will give you an approximate measure of your throughput.
There is no dearth of applications if you want more network-related metrics to assess your internet performance. I’ll list a few of them here.
- Paessler Network Latency Sensors with PRTG (Has a 30-day free trial)
- SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor (30-day free trial)
- SolarWinds Ping Sweep with Engineer’s Toolset (14-day free trial)
- Site24x7 Network Monitoring (30-day free trial)
- ManageEngine OpManager (30-day free trial)
- Iperf (Open Source)
- Netperf (Free)
- NetScan tools
Frequently Asked Questions
Does latency affect throughput?
Yes, latency affects the throughput. The higher the latency, the longer it takes for data to reach its destination, affecting the throughput.
What is latency measured in?
The latency is the time taken for a packet to reach its destination. It is measured in milliseconds.
Is throughput the inverse of latency?
No, throughput is not the inverse of latency. Latency is the time taken irrespective of the volume. While throughput is the measure of the volume of data in a unit of time.
What latency is good?
A latency of 20-40 ms is ideal. Latency above 100ms will have a considerable effect on your gaming experience. The lower the latency, the faster the data flow, which translates into good streaming and gaming experience.
Conclusion
Throughput and latency are essential metrics to measure your network performance, which also rely on the capacity of the networking device in use. A clear idea of these metrics will help you spot and fix the lags in performance and get the most out of your internet.
