Megabit vs Megabyte (Mb vs MB): What Are The Differences?

If you haven’t been confused before between megabit and megabyte, you might have been living under a rock in this era of tech and the internet. We use them in measuring the data, but they are not the same.
Megabit, abbreviated as Mb, refers to the speed w.r.t data transfers, i.e., internet speeds. While Megabyte, aka MB, is used to measure data w.r.t storage devices, i.e. size of files, the storage capacity of your RAM & HDD.
It can get confusing, as we abbreviate both as Mb vs MB, with the only difference in capitalization. This article intends to clear the mist of doubt around the terms and ensure you understand & use them in the right context.
Megabits vs Megabytes (Mb vs MB)
What is a Megabit?
A megabit equals 10^6 times the unit bit. It is abbreviated as Mb or Mbit.
What is a Megabyte?
A megabyte equals 10^6 times the unit of measure byte. It is abbreviated as MB or MByte.
Bits vs Bytes
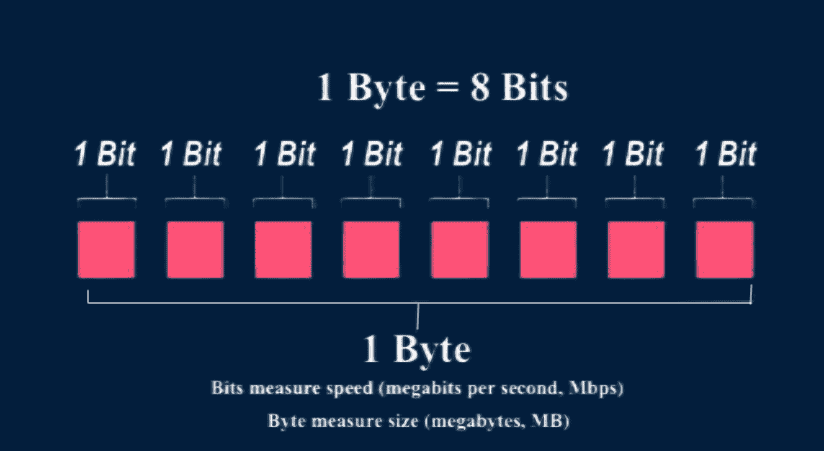
The bit is a term used to measure the smallest data unit in computers and digital information. A bit is a binary digit represented as 0 (Off / No) or 1 (On/Yes).
Whereas byte is the basic unit of measurement in computer storage and processing. A byte represents a group of 8 binary digits (bits).
Bit vs Byte is 1:8 expressed in terms of ratios. This applies across all the units of measure.
1 Byte = 8 Bit, 1 Kilobyte (KB) = 8 Kilobits (Kb), 1 Megabyte (MB) = 8 Megabits (Mb), 1 Gigabyte (GB) = 8 Gigabits (Gb) so on and so forth.
Megabits Per Second vs Megabytes Per Second (Mbps vs MB/s)
The term Megabit per second (Mbps) is used to refer to your internet speed. Higher the number, the faster your internet connection.
The Megabytes per second (MB/s) is used to refer to the data read/write speeds to and from your hard disk or any storage device. The higher the number, the quicker the data transfer speed from/to your device.
MBps is the faster speed compared to Mbps. But context and conversion are essential. When your ISP sells an internet package, the measure of transfer speed is megabits per second (Mbps). Regarding storage units (file size), you will download at a speed of 0.125 Megabytes per second (MBps).
If you download a file of size 1GB via a 100 Mbps speed plan, you will download the file at 12.5 MB per second, not 100MB per second. Don’t mix & match these terms and end up paying extra or expecting unrealistic download speeds.
Keep this clear 1 MBps = 8 Mbps or 1 Mbps = 0.125 MBps.
Megabytes To Megabits Calculator
The easiest way to convert megabytes to megabits is to multiply the units by 8.
- 1 Byte = 8 Bits
- 1 Megabyte = 1000000 bytes
- 1 Megabyte = 8000000 bits
For the sake of convenience and as a common standard of measure, the data is further divided and measured in 1000s
- 1000 bits/bytes = 1 Kilo bits(b)/bytes(B)
- 1000 Kb/KB = 1 Mb/MB (Mega)
- 1000 Mb/MB = 1 Gb/GB (Giga)
- 1000 Gb/GB = 1 Tb/TB (Tera)
For further clarity, look at the table, which keeps the megabit as the unit of reference and equivalent in Bytes.
Also check: Is Gigabyte or Megabyte bigger? [GB vs MB]
Different Internet Speeds
Frequently Asked Questions
Which is faster, megabyte or megabit?
Regarding data transfer speeds or read/write speeds, a Megabyte is faster than a megabit. 1 Megabyte equals 8 Megabits.
Is 100 MB the same as 100 Mbps?
No, they are not the same. A 100MB read as 100 Megabytes is a measure of data size. 100 Mbps, read as 100 Megabits per second, is the speed or rate at which data is transferred in the internet/intranet.
Which is bigger, MB or KB?
An MB (Megabyte) is bigger than KB(Kilobyte). The conversion ratio is 1:1000. One megabyte equals 1000 Kilobytes.
How many megabits are in a megabyte?
There are 8 megabits in a megabyte.
What’s bigger, MB or GB?
A GB (Gigabyte) is bigger compared to MB(Megabyte). One Gigabyte equals 1000 Megabytes.
What does MB stand for in file size?
An MB, as a measure of file size, stands for Megabytes.
To sum up, Megabits and Megabytes are not the same. When paying for a storage device or your internet plan, ensure you get the unit of measurement right. I hope this article has cleared up the difference between megabits and megabytes.
