Mesh WiFi Buying Guide: How To Choose One in 2025?

Mesh WiFi systems have gained immense popularity, and their compound annual growth rate is expected to rise by 8.8% from 2020 to 2025.
Mesh networks are designed to improve the internet experience with seamless coverage throughout the house. However, finding the best mesh system for your needs can be a headache.
If you’re a network newbie or a non-techie person who wants to learn how to choose a mesh WiFi, you have come to the right place. In this mesh WiFi buying guide, I shall discuss all important terminologies, aspects, and features to consider.
So without any further delay, let’s get going!
Key Factors To Look for in a Mesh WiFi System
- Wireless Standard: Wi-Fi 5, 6, and 6E are a set of specifications for Wi-Fi connectivity, Wi-Fi 6E is the latest among them. The higher the standard, the more future-proof the system.
- Coverage & Mesh Nodes: Mesh systems are available in 2-Pack or 3-Pack. So, calculate your space area and select a variant accordingly. You can also add a separate mesh node in future.
- Frequency Bands: There are three types of mesh systems, i.e., dual-band, tri-band, and quad-band. As the name suggests, dual-band comes with two bands (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz), tri-band with three, and quad-band systems with four bands. The greater the band, the more channels and faster the data transfer.
- Speed Capacity: The maximum speed capability of these systems has now gone as high as 14 Gbps, but everything comes at a cost. Just make sure your system can handle your internet plan and needs.
- Devices Capacity: Calculate the number of devices and users that need internet connectivity at your home. Choose a mesh system that promises a higher number of supported devices.
- Port Setup: Most mesh setups come with limited ports, particularly, USB ports. Ensure the system you choose has the required ports for your setup and needs.
- Security Features: Most systems boast the latest WPA3 encryption and VPN-passthrough that keeps your datasets secure. Also, look for additional features like parental controls, filters, scheduled access, and more.
- Setup & Management: Thankfully, most mesh systems are easy to set up and manage, courtesy of the companion app of each manufacturer.
- Additional Features: Some mesh WiFi systems are Alexa and Google Assistant compatible. Meaning, you can control them using voice commands. It adds convenience to smart homes.
Also interested in learning about how to choose a traditional router? Read my wireless router buying guide.
What Is Mesh WiFi?
Mesh WiFi is a whole home WiFi router system that eliminates all network dead zones in your space and delivers an uninterrupted network throughout the house.
How Does Mesh WiFi Work?
Mesh WiFi is different from Wi-Fi extenders and Access Points. What separates mesh from them is that mesh networks are intended to provide seamless connectivity (without a signal drop) in every corner of your house.
Here’s how a mesh WiFi works: A single router unit acts as the main hub that sends signals to other units, which are also known as nodes or satellites. The nodes/satellite units capture the signals and rebroadcast them throughout the house.
How To Choose A Mesh WiFi System?
Choosing a mesh WiFi is not rocket science, but there are a few things to consider before getting one. I’ve explained them in detail in the following sub-sections.
1. Wireless Standard
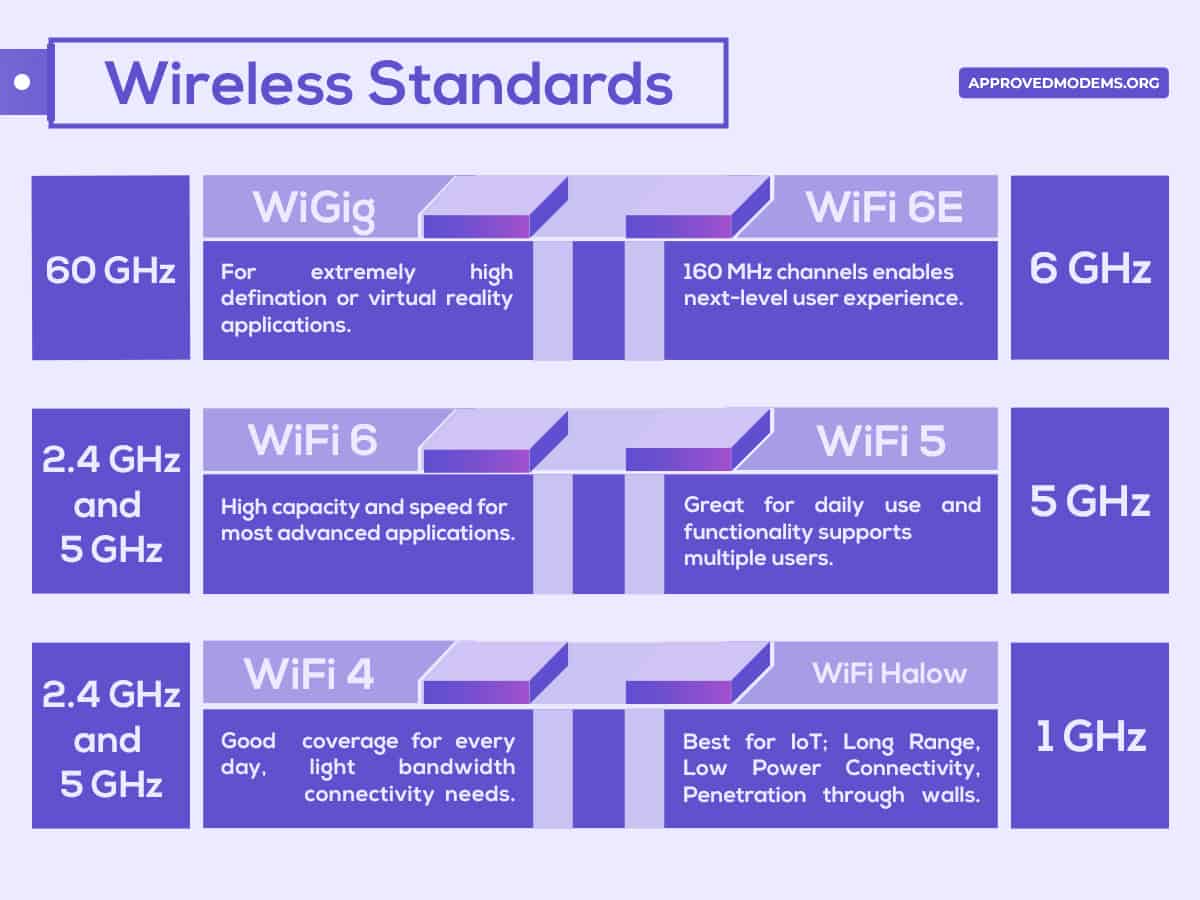
Wireless standards are a set of protocols and standards that dictates how your wireless network acts. The most prevalent standards are IEEE 802.11 WLAN (Wireless LAN) and mesh, and IEEE updates these standards every few years.
Now the time I am writing, 802.11ax (for Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E being the latest) is the popular standard in most routers, whose previous version was 802.11ac for Wi-Fi 5. And as mentioned in my WiFi 5 vs WiFi 6 comparison, the latter is 1.3 times faster than its previous generation.
Now, networking companies plan to roll on the next generation standard, 802.11be, with the name Wi-Fi 7. The routers have more bandwidth and channels, so they transfer data faster and easily cut through congestion.
The AX routers are future-proof to work well with any high-speed plans that currently exist or will be launched in the future. Besides speed, they have various added functionalities to boost their overall capacity, performance, efficiency, and security.
P.S. Get a router with the latest WiFi standard to reap the benefits of high-speed plans in the present and future.
2. Frequency Bands & Channels
Before I dive into recommending which frequency bands should you look into your mesh system, let me explain what they actually are.
These are a series of radio frequencies that carries data in a wireless spectrum and are further broken into Wi-Fi channels.
Mesh systems or standard wireless routers are distinguished by the bands they integrate. Dual and tri-band routers are available for purchase in the retail space, where dual band integrates one 2.4 GHz and one 5 GHz band. While there’s an extra 5 GHz band in tri-band units. Here’s how 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz compare.
Note: In the new series of WiFi 6E mesh setups, the 6 GHz band replaces the standard 5 GHz.
As explained above, each band integrates a certain number of channels within them, and the higher the band value, the more channels are there.
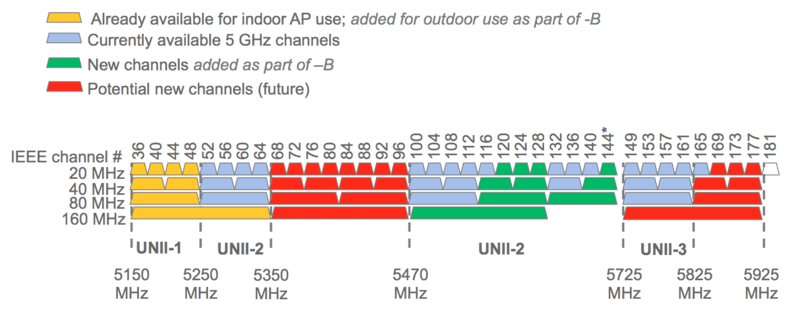
- For example, the 2.4 GHz band has 11 channels, each with a 20 MHz width.
- While the 5 GHz band has 45 channels with a 40-80 Mhz width.
- Similarly, the latest 6 GHz band has 60 channels, with each 160 MHz wide.
The greater the number of channels, the network has more scope to travel through, therefore, the more bandwidth on offer.
Besides that, some mesh systems like Google Nest WiFi have an advanced feature called band steering that automatically steers bands depending on real-time congestion. In other words, data always passes through the least congested band/channel, and you get access to fast internet throughout the day.
3. Speeds & Compatibility with Plans
When you step forward to choose an ideal mesh WiFi, it’s important to remember that one size doesn’t fit all. Every unit exhibits different bandwidths or data-transferring capabilities.
So, if a router’s maximum speed limit reads 1600 Mbps, you can go gaga the whole night using such high speed. But that’s the maximum you get from a router, which actually depends on your monthly service plan.
The service pack of your ISP limits the actual and maximum browsing, downloading, and uploading speed. There are many trendy and flamboyant models out there, but the bottom line is speed has nothing to do with it, and you must check the actual specifications during purchase.
Although a lightning-speed-generating router doesn’t influence your internet speed directly, but it is enough to give pace to the internal network.
4. Mesh Nodes, Coverage, and Devices Capacity
Mesh systems generally come in a two-pack or a three-pack unit, where one serves as a central hub to dissipate signals to the nodes, which are further sent to another node.
When there are no more nodes to communicate, signals are forwarded to the connected devices. In turn, nodes act as satellites, so the more powerful the nodes, the farther the signals reach.
Many high-end mesh systems have advertised a reach of around 6,000-8,000 Sq Ft of space, which is massive. But that results in ideal settings, which vary from home to home and your surroundings.
For example, the emitted signals are disrupted by 25-30% if your home has thick concrete walls or metal frames or multiple networking devices working concurrently. So, if your place has a lot of physical obstructions, choose mesh systems that are good for thick walls.
Other than that, the specifications of your client devices also affect their network-receiving ability. For example, laptops have better antennas or wireless capability than smartphones and, therefore, can receive signals from a distance.
5. Ports & Connectivity
Almost all mesh systems have physical ports, including Ethernet and USB. Ethernet ports are handy if you have bandwidth-hogging devices to connect and get to experience the fastest network connection.
Compared to standalone WiFi routers, mesh systems have lesser Ethernet ports, but if you have many devices to connect, ensure having at least three ports on each unit. Other than that, there are USB 3.0 ports in some that let you connect a shared storage device or peripheral devices to transfer faster data.
I’ve published a dedicated article on mesh WiFi systems with more ethernet ports.
6. Important Terms & Technologies
1. MU-MIMO
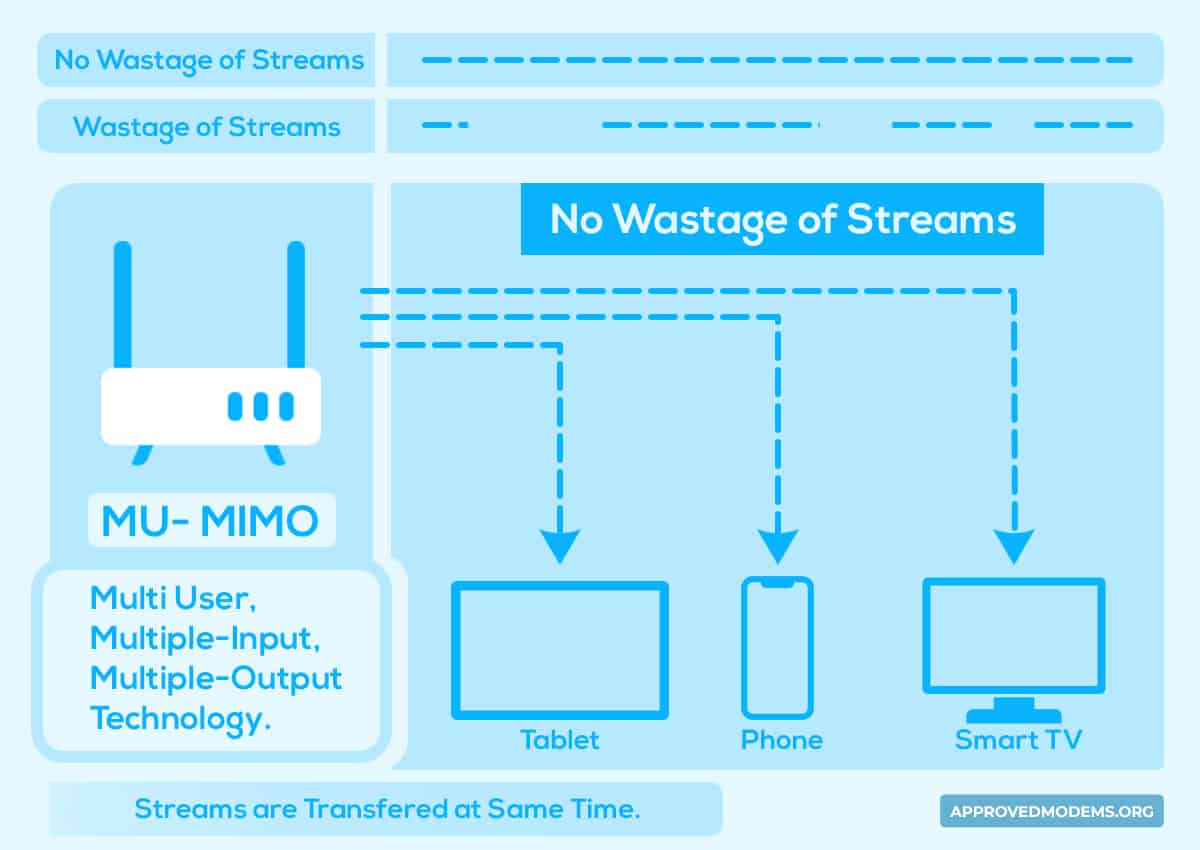
MU-MIMO, better known as Multi-user, multiple-input, multiple-output technology, lets a mesh router communicate with a multitude of devices concurrently. So, devices don’t have to wait much to receive signals, and speeds are dramatically increased.
Technically speaking, MU-MIMO splits the datasets into small packets, each with a separate bandwidth. So rather than needing to carry a large chunk of data, respective channels can now transfer data much faster. The maximum carrying capacity of Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6 are four and eight, respectively.
For your eight devices battling for bandwidth simultaneously, MU-MIMO should enhance your WiFi experience.
2. OFDMA
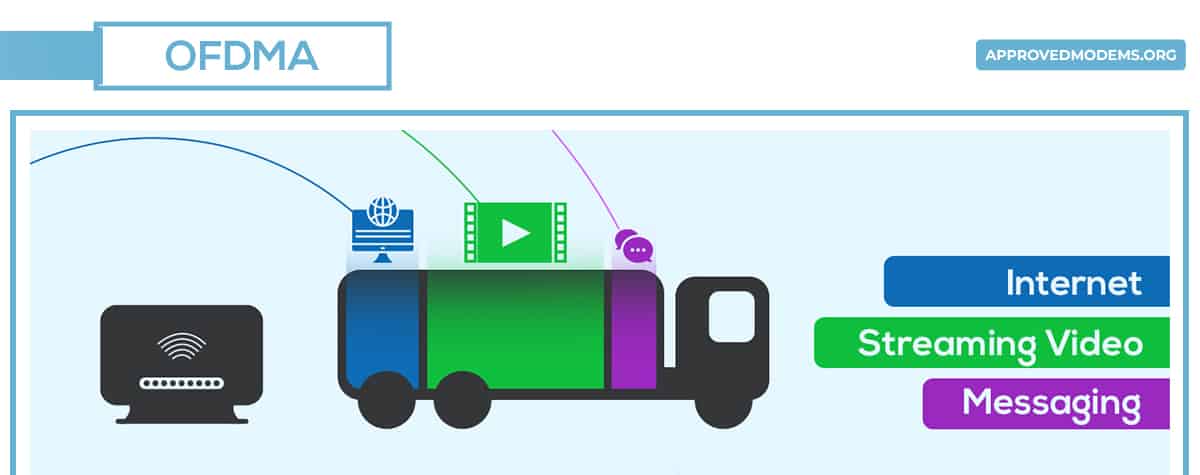
OFDMA, better known as Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access, is the latest technology introduced in Wi-Fi 6 routers to fulfil the varying bandwidth needs of users.
I have used delivery trucks as an analogy to understand how it works. With Wi-Fi 5, each truck or channel could carry the load for a single user at a time. But with OFDMA in Wi-Fi 6, it’s possible to carry different loads for varied users.
Other than that, the drop-off schedule or bandwidth transmission rate is optimized for increased speed and performance.
3. Beamforming
Beamforming is a technology that directs the signals specifically toward the receiving device rather than dissipating the signals in all directions. The resulting connection is now more reliable and faster as it’s without beamforming. With beamforming in your mesh, the devices are bound to boost WiFi range through walls.
4. Backhaul
Backhaul is a term used for communication between a mesh system and its nodes/satellites. Unlike single routers with limited coverage, whole home routers can dissipate signals much longer, courtesy of seamless communication between the main router and its satellites.
These systems use a dedicated backhaul band to communicate with the nodes, so it doesn’t compete with client devices for bandwidth. Other than that, you can also create an Ethernet backhaul by physically connecting your mesh system to its satellites.
This setup improves backhaul performance, especially in budget devices, but it’s inconvenient to set up. Overall, a dedicated backhaul Wi-Fi gets you the best of both worlds with great performance and easy setup.
7. Security Features
Now with multiple devices connected and millions of datasets carried over the network, the mesh system must have requisite security features in place.
With these units installed, you don’t have to worry about encryption with integrated WPA2/WPA3 encryption coming right out of the box. These latest standards keep the data shared secured by keeping them encrypted.
Most importantly, whole home routers install security updates automatically and to other small network pieces. It means existing security flaws like the KRACK vulnerability, revealed a few months back, are patched across the network without much intervention.
That’s not the case with single routers with Wi-Fi extenders that needs you to make updates manually when required.
Some parental controls are also part and parcel of these devices. Today’s digital mothers can now monitor and manage their kids’ detailed online activities. There’s also an option to block potentially explicit or malicious websites and pause your WiFi anytime.
Moreover, some notable router companies like Netgear, TP-Link, ASUS, and others offer multiple customizations and upgrades for a few extra dollars.
These paid security suites ingrain some advanced features like establishing a firewall, identifying malicious websites, blocking attackers, and many others. You can choose to upgrade your security if you need one.
8. Mesh Setup & Management
Some old routers can only be set up by connecting a modem to the laptop/PC, and accessing the web interface. Sometimes, the process can get tiring and complicated, especially if you’re a newbie. Modern mesh systems have brought a solution with easy-to-use mobile apps.
These apps are available for free on multiple platforms, Android or iOS, and let you be done with the installation process in no time. Specially designed for newbies, these apps come with detailed instructions (video/written) that you must follow to get it done.
Apart from that, these apps come with many other functionalities to provide complete control over the router in your hands. You can set up access points, manage devices, and toggle through security settings and parental controls.
9. Hardware & Internals
The hardware & internals is as important as the software and the technologies it integrates. Its internal components include flash memory, RAM, and a Processor.
A mesh router must boast at least a Dual-Core processor, 128MB RAM, and 128MB flash memory for it to deliver a satisfactory performance level in any setting.
The processor is like a brain that communicates and produces bandwidth to be sent out to the devices. At the same time, RAM and flash memory are used to store temporary datasets to be sent to the processor when required. All of these work harmoniously with other components to deliver a powerful performance.
Mesh Network Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Mesh WiFi
- Mesh routers don’t need additional routers, and each node acts as a router itself. It means you can change the network size quickly and easily.
- Each node receives millions of data in encrypted form and translates them. It provides a lot of redundancy, which keeps the mesh system running even if any problem arises.
- With nodes connected, signals from the main hub travel long distances. Coverage of some devices can go as high as 8,000 Sq Ft.
- It integrates some latest technologies like OFDMA, MU-MIMO, and beamforming to send signals to multiple devices without losing speeds by much.
- Most mesh units integrate the latest security standards, WPA2/WPA3, and VPN passthrough to keep your shared data safe and secure.
Disadvantages of Mesh WiFi
- Each node has to send the received messages, act as a router, and track messages throughout the day, which increases the complications by a notch.
- Finding the right place for your router and satellites is crucial in dictating the overall coverage, and the process is a bit more tricky than it seems. It’s important you keep the main hub and nodes at a distance to experience a seamless connection throughout your space.
- A low-power network can have latency issues and therefore need you to upgrade the entire mesh system.
- Each node needs a power source to run.
- These systems cost much more than a traditional single router.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should I look for when buying a WiFi mesh?
Here are a few things to consider:
- Select a mesh system with at least a Wi-Fi 6 as the wireless standard if you need the fastest speeds on your client devices.
- Check if your selected device has enough bandwidth to support your network needs.
- Measure the area of your home that needs covering, and get a unit accordingly.
- Make sure the mesh wi-Fi has adequate security and parental controls.
- Check if the provided app is user-friendly.
How big of a house do I need for mesh WiFi?
Mesh systems are suitable for users with a house area of at least 3000 Sq Ft. So any house with a similar area or more should require a mesh system.
What are the disadvantages of mesh WiFi?
Here are a few disadvantages of mesh WiFi:
- Mesh systems are expensive
- Placements are tricky
- Each node needs a power source to
Is mesh WiFi better than an extender?
Even though both Wi-Fi extenders and mesh Wi-Fi do the job of improving wireless coverage, mesh routers are much smarter. They work much harder to boost your overall performance and cover a larger distance than extenders. So, in short, mesh Wi-Fi is a clear winner between the two.
Is mesh WiFi really worth it?
Based on the Wi-Fi performance, you can’t go any wrong with a mesh router in terms of both speed and coverage. Suppose you reside in a smaller apartment or have a small office; some aspects make a router less effective. These are thick concrete walls, metal frames, or the presence of multiple networking devices. This is where mesh routers offer a smoother experience.
Can I add mesh WiFi to the existing router?
While yes, you can add mesh Wi-Fi to your existing router, it would be better to replace your router with a new mesh router. These devices use two or more nodes or satellites to distribute the signals throughout your home, thereby delivering solid Wi-Fi coverage. It is designed to deliver an effect similar to multiple routers.
Conclusion
Getting a mesh router is easier than it seems to be, but there are a few things you need to keep in mind while making a purchase. I hope this mesh WiFi buying guide helps you make an informed decision.
