In this post:
- Powerline Adapter vs WiFi Extender: Key Differences
- What is a Powerline Adapter?
- What is a WiFi Extender?
- WiFi Extender vs Powerline Adapter: Detailed Comparison
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Powerline Adapters
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Wi-Fi Extenders
- TL;DR [Key Takeaways]
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Do you have weak Wi-Fi signals in parts of your house? Is your internet-usage experience taking a hit because of it? Are you stuck in a dilemma choosing between a powerline adapter and a WiFi extender? If so, you've arrived at the right place.
Both improve your coverage, but they differ in functionality, signal quality, speed, consistency, installation, and of course cost. Let's discuss them all in detail.
Powerline Adapter vs WiFi Extender: Key Differences
A powerline adapter uses the existing electricity wiring of your home to transmit the data signals. The Wi-Fi extender captures the wireless signals and re-transmits them.
| Feature | Powerline Adapter | Wi-Fi Extender |
|---|---|---|
| Mode of transmission | Wired(Electricity cable) | Wireless |
| Type of interference | Electric noise | Radio and physical obstruction |
| Setting customization | No | Yes, Possible |
What is a Powerline Adapter?
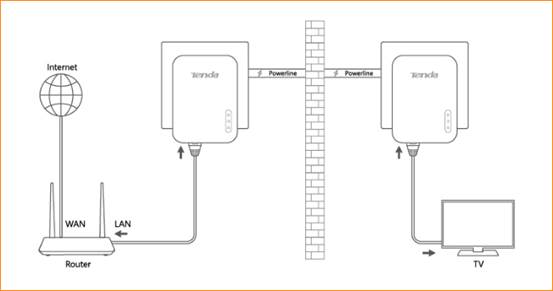
A powerline adapter works in pair. A primary adapter is wired to the main router. It converts data into electric impulses and sends them to your existing electric wiring. An adapter on the other end, filters and decodes the electric signals into data. Which is then delivered to a device via an Ethernet port or WiFi.
For more details, learn how powerline adapters work.
What is a WiFi Extender?
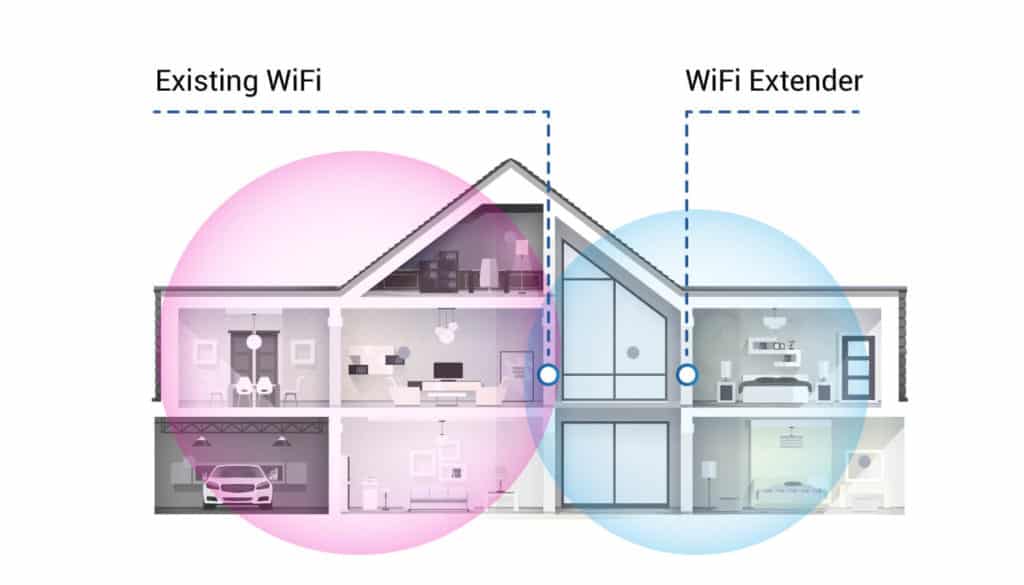
A WiFi extender relies on wireless channels to improve your coverage. With the help of internal or external antennas, the wireless signals from the primary router are captured and re-transmitted. This helps you improve the reach of the internet.
WiFi Extender vs Powerline Adapter: Detailed Comparison
This section will give you a detailed comparison of the performance of both powerline adapters and WiFi range extenders across different factors.
1. Functionality (How It Works)
The WiFi range extender uses radio antennas to capture the data from the main router and relays it further to the client devices.
While a powerline extender is wired to the router, which then converts the data into electric impulses and transmits them to electric wiring. A powerline is better in this regard, considering it uses a wired medium to get the data from one point to another, which is prone to reduce latency and improve reliability.
WiFi extender uses a wireless frequency, that is prone to interference from multiple sources, impacting its stability.
2. Coverage & Signal Quality
A Wi-Fi extender captures the signal from the router and repeats them. It doesn't strengthen or amplify them. Stronger the signal from the router, the better the output from the extender.
This demands the proper place for the extender to remain close to the router, mid-way between your target area and the source. Keeping that in mind, an extender with 1000 sq ft coverage will potentially extend the signals up to approximately 500 sq ft. It is helpful when you are targeting wireless devices in a specific area.
With powerline, it is easier to target specific devices or rooms without worrying about the distance from the router. Although the longer the distance the data travels through the electric wiring, the higher the chance of interference and speed loss.
If a powerline extender has Wireless radios to transmit wireless signal at the receiving end, it has a higher coverage potential. In this case better than a Wi-Fi extender, which relies on the proximity to pick up signals from the router.
3. WiFi Speeds
Both powerline adapters and Wi-Fi extenders are bound to lose speeds, for the same reason. They use a shared medium, albeit different ones.
Wi-Fi extender uses wireless channels, which are teeming with signals from the router and other client devices. This makes it vulnerable to interference. Add physical interference of the walls, and appliances, which further worsens the speeds.
A powerline extender on the other hand relies on the quality of the electricity wiring. The wiring is shared with other electrical appliances across the household. Fluctuations in consumption and proximity to heavy electric devices determine the speeds at our disposal.
👉 Related Reading: 7 Best Powerline Adapters for Gaming in 2025 [Low Latency]
A WiFi range extender fares better in delivering higher WiFi speeds, yet fluctuations are inevitable. But if you're chasing consistency, a powerline adapter leads the race.
4. Performance & Reliability
If your activities are limited to social media, surfing, listening to music, and calls, a Wi-Fi extender might just be adequate. You will hardly notice the drawbacks of using a shared wireless space. It applies to a powerline extender, lest your internet activity is data-heavy.
That's when the downsides come into play. Latency measured in ping is an essential metric for gaming performance. A Wi-Fi extender is vulnerable to high latency as it uses the same wireless frequency to transmit data back and forth.
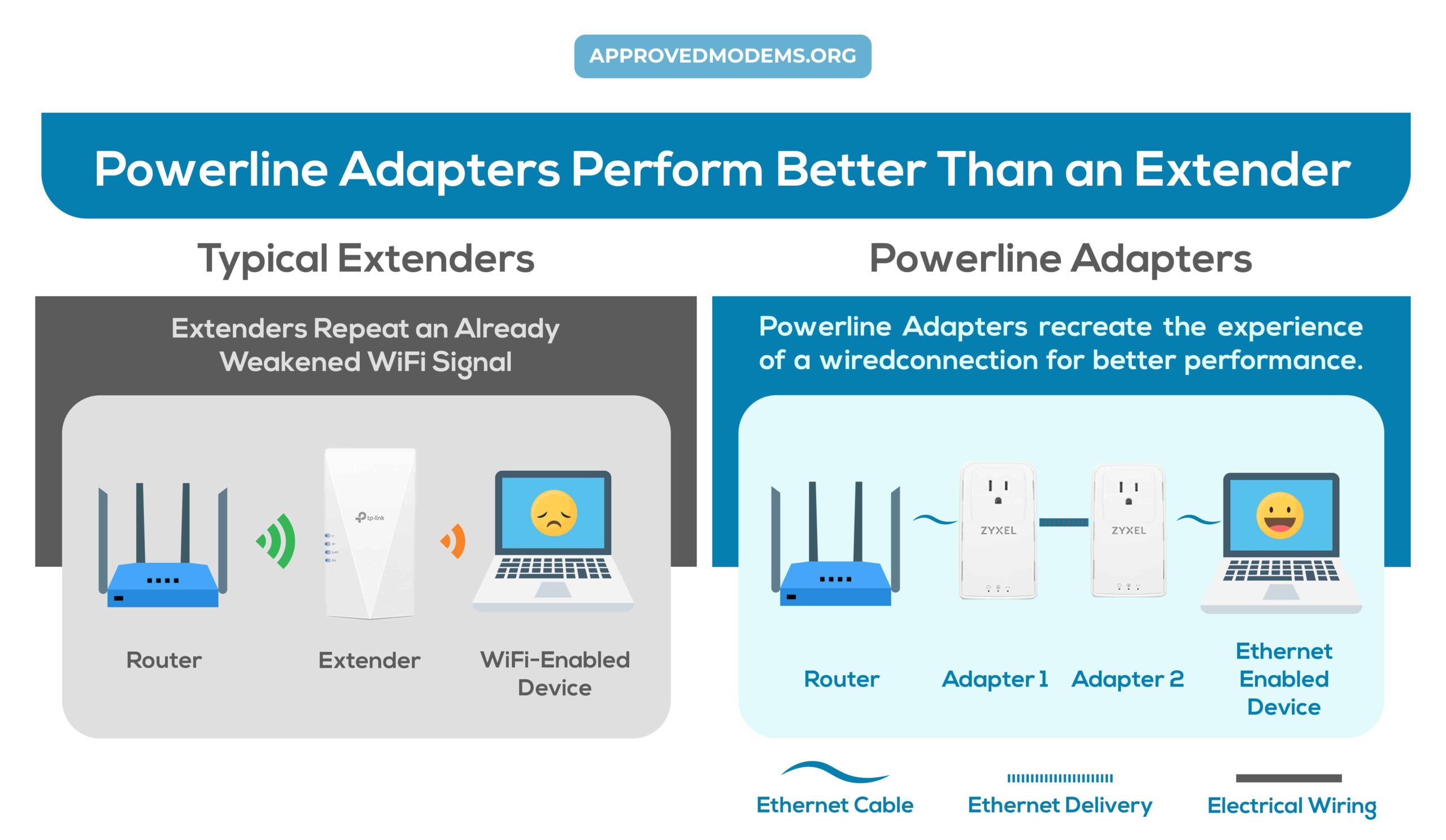
The powerline adapter, despite being shared, is a wired medium. It is less vulnerable to latency as compared to a WiFi extender, hence has a better chance of delivering a good gaming performance.
The performance also depends on the device-specific hardware. Both devices have quite a lot of choices in the market, and it's imperative to choose the right device. If you're not sure which one to pick, you may check the following resources:
- Best all-around WiFi extenders
- Best WiFi extenders for gaming
- Best dual-band WiFi extenders
- Best WiFi extenders for garage
- Best WiFi boosters for RV
- Best WiFi extenders for basement
- Best WiFi extenders for security cameras
- Best WiFi extenders for home use
- Best WiFi extenders for Ring cameras
- Best WiFi extenders for long range
- Best Ethernet WiFi extenders
- Best WiFi extenders for outdoors
- WiFi extenders for Comcast Xfinity
- WiFi extenders for Spectrum
- WiFi extenders for Cox
- WiFi extenders for Optimum
- WiFi extenders for CenturyLink
- WiFi extenders for Google Fiber
- WiFi extenders for Frontier
- WiFi extenders for AT&T Fiber
- WiFi extenders for Verizon FiOS
- WiFi extenders for Starlink
- WiFi extenders for Kinetic Windstream
5. Cost vs Value
Both the Wi-Fi extender and powerline adapters are cost-effective alternatives to mesh WiFi systems. They are available for as low as $30 with no additional installation or infrastructure costs tagging along.
While you can get a Wi-Fi extender stacked up with advanced features catering to the requirement on the premium end of the spectrum, it's hard to find a powerline extender that incorporates all the latest technology. An area where a Wi-Fi extender seems to be a better option.
6. Installation & Management
Concerning installation, both the Wi-Fi extender and powerline are easier to install. They are plug-and-play devices. Both are up and running with a touch of a single button in less than a few minutes.
As it boils down to management and customization, a Wi-Fi extender fares better.
You'll be able to customize your priority, set bandwidth, and schedule usage, according to your requirements. With a powerline extender, that would be hard to achieve. You're more likely to use the device in its default configuration.
👉 7 Best WiFi Extenders for Gaming in 2025 [Low Ping]
7. Reliability & Scalability
Neither the powerline adapter nor the Wi-Fi extender can be reliably scaled up. A powerline adapter is capable of working with multiple nodes. If the capacity of the primary extender is low, adding additional nodes would leave an adverse effect.
The effect of scaling up additional nodes even with high capacity may not have the intended effect, as it is contingent on the electricity usage.
Adding more WiFi extenders to the router would make the network more congested, affecting its performance.
Yet, when you have larger surface areas to cover, the performance of a Wi-Fi extender wouldn't have an adverse effect as much as a powerline extender. Most Wi-Fi extenders are universally compatible and work with multiple routers, irrespective of the OEM.
From experience, it's never the case with powerline extenders. More often than not, compatibility becomes an issue when it comes to different OEMs., which makes Wi-Fi extenders a tad more reliable.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Powerline Adapters
Pros
- Saves the hassle of drilling holes for new wiring installations.
- Wired connectivity at affordable pricing.
- Quick setup with a touch of a single button.
- A plug-and-play design that makes it flexible to move around within the household.
Cons
- Loss of speed is imminent as the wiring is shared across the entire household & appliances
- Works only within the same electric circuit or phase.
- The longer the distance between the adapters, the higher the latency & lower the reliability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Wi-Fi Extenders
Pros
- Improved wireless coverage
- No additional installations
- One-touch set up
- Budget-friendly
Cons
- Vulnerable to physical and network interference
- High latency; not suitable for gaming
- Reduced speeds
TL;DR [Key Takeaways]
- Both Wi-Fi extenders and powerline adapters use a shared medium to transmit data, albeit differently.
- They’re both vulnerable to multiple external factors
- Powerline extenders are better for gaming
- Wi-Fi extenders are easier to customize and manage
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, given you have modern quality electricity wiring, a powerline extender brings the best of both worlds. An easy setup without any installation and the stability of wired connectivity.
A Wi-Fi extender cannot be used as a powerline adapter. A WiFi extender captures wireless signals and re-transmits them, but a powerline adapter is designed to convert data to electric signals and convert them back to data.
Being a wired connection, a powerline adapter is well-suited for gaming than a Wi-Fi extender, which is prone to physical /radio interference and high latency.
No, the powerline adapter wouldn't work on an extension cord. For a powerline adapter to work, both adapters should be on the same wiring circuit.
Conclusion
Both powerline adapters and Wi-Fi extenders are cost-effective solutions, when running Ethernet cable isn't feasible. If you are not into gaming, a Wi-Fi extender would be a more flexible option for extending the network.
If gaming performance is essential, you're better off using a powerline extender on modern electric wiring.





