Wi-Fi network security is the key to protecting devices and confidential data on your network. It starts by getting a security-focused router, creating stronger passwords and the latest encryption standards, and reinforcing them with industry best practices.
Any wireless network is vulnerable to unauthorized access and DDoS attacks. It leads to a loss of internet bandwidth, poor performance, identity theft, loss of privacy, and data leaks that might cause financial loss.
Worry not; this article gives you an overview of imminent threats and practices that will help you avoid them and secure your wireless network.
Threats for Wireless Networks
Let’s look at the most imminent threats to which a wireless network is susceptible:
1. Unauthorized Access/War Drivers
Wireless networks disseminate signals/beacons to announce their existence to allowed users, allowing them to identify them. War drivers use a combination of high-gain antennas and software to look for vulnerable networks and devices.
A vulnerable network will fall prey to attack, allowing exploitation of bandwidth and also the potential of compromising information shared within the network.
2. Traffic Monitoring & Eavesdropping
As wireless communication happens via radio waves, it allows hackers to monitor and analyze the traffic and its content. Even from a hundred feet, snoopers or eavesdroppers can decode sensitive data, including usernames, passwords, and financial transactions, putting you at risk of potential financial or reputation loss.
3. Denial of Service attacks
Wireless networks operate on limited capacity contingent on the hardware in use. The denial of service attack over a WiFi network robs the intended users of access to your resources. The perpetrator sends a huge amount of traffic noise and overwhelms the networking device, and disrupts service.
4. Spoofing & Session Hijacking
Spoofing is an act of masquerading non-trusted network traffic as being from a trustworthy source. By using multiple spoofing techniques, an attacker gets access to a random user's web session, termed session hijacking.
This will allow access to private confidential information, making every gadget connected to the wireless network vulnerable to similar attacks.
5. Rogue Access Points
One technique often employed by attackers involves producing an access point within the coverage area of another wireless network.
This opens up the chance for users to connect to the access point, allowing them to gain access to a device and all the information that comes with it.
6. Evil Twin attacks
This attack builds on the idea of creating a rogue access point resembling a legitimate wireless network. When an unsuspecting user joins the fake point, it compromises the device and the information communicated over the wireless network.
7. Wireless Sniffing
When you are using public WiFi networks that are not secured, the internet traffic is not encrypted. This will make all communications via the device vulnerable to attack. Malicious users can use dedicated tools to retrieve sensitive information and use it for their gain.
How To Secure a Wireless Network?
In this section, you'll learn about the most effective practices that help you navigate most of the wireless threats discussed in the section above.
Securing WiFi networks requires practices that involve creating effective access control and keeping wireless communication private.
1. Change SSID & Password

Leaving your router's default SSID and password would make it easy to gain access. Personalizing the SSID and changing the default password is the first step in securing a wireless network.
You can further improve the security by using WPA2 or the latest WPA3 encryption protocols. While disabling SSID broadcasts will keep your SSID hidden and keep away the freeloaders from trying to connect to your network.
The router's admin password remains the same for routers across the same OEM. Change the default password to avoid a scenario of anybody else connected to the network taking control of your router.
Note: Funny WiFi names aren't vulnerable to network security as long as you're not revealing a password or hint in it.
Steps to Change SSID and Password:
- Login to the router's admin portal
- Navigate to the wireless settings
- Enter the New SSID and passphrase as highlighted
- Uncheck the Enable SSID broadcast to disable broadcast
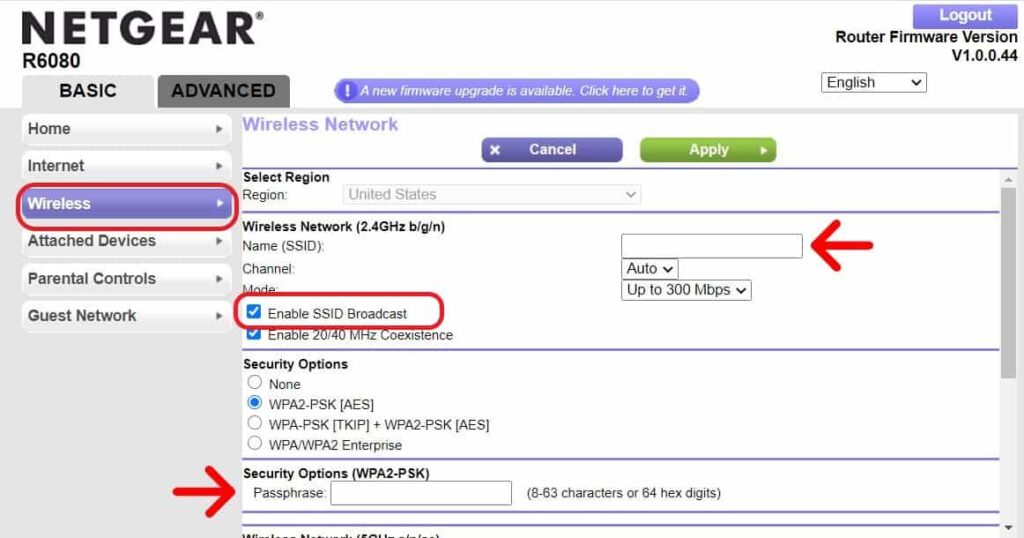
- Click Apply
2. Start Using the Guest Network
If an infected device is connected to your wireless network, anyone with access to the device can get the information connected to your home WiFi network.
Using a guest network for external devices will keep those intruders away from the home network and minimize the chances of any further attack.
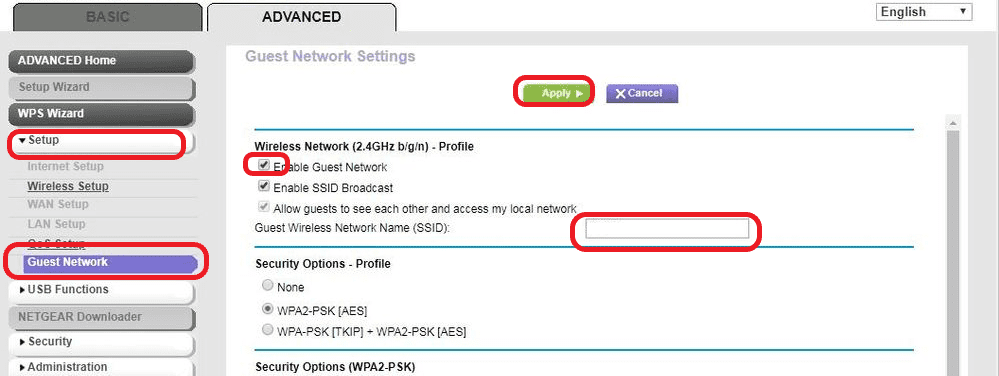
Steps to Configure Guest Network:
- Login to the router's admin portal
- Go to Advanced settings
- Click on setup and Navigate to Guest Network
- Click the enable guest network checkbox
- Enter the guest network name and apply the settings
3. Configure a Firewall
Configuring a firewall in the router will improve the wireless network drastically. A firewall assists you in monitoring incoming traffic. This can prevent attacks arising out of unauthorized applications, malware, and malicious content.
Steps to Configure a Firewall:
- Login to the router's admin portal
- Go to advanced security settings
- Click on the Security menu
- Choose firewall rules
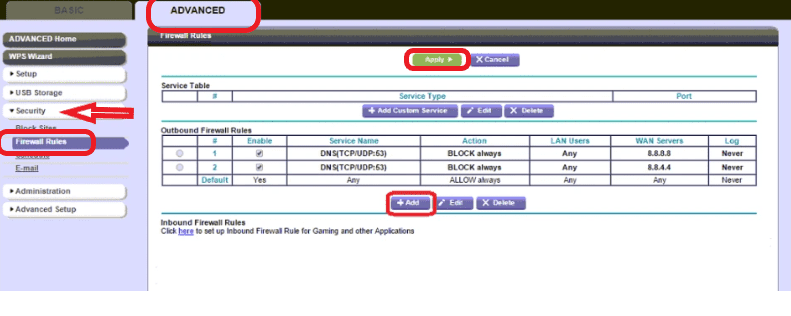
- Add custom services and application traffic that you want to allow by clicking on Add button
- Save the settings by clicking on Apply
Note: Some routers come with a built-in firewall. You may upgrade to one of them as they're great routers for small businesses.
4. Use a MAC Filter
Another practice to improve your wireless network security is incorporating MAC filtering. Every device accessing a wireless network has a MAC address to identify itself.
By limiting the access to devices in your MAC white list, you can limit any external device connecting to your WiFi network and accessing the internet.
Steps to using a MAC Filter:
- Login to the router's admin
- Go to Basic settings
- Click on the Attached devices
- Ensure the check box for blocking all new devices from connecting is selected
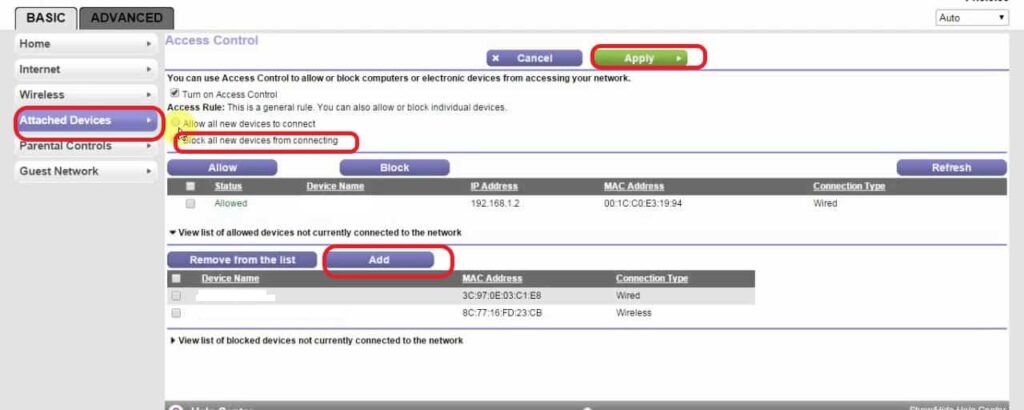
- Click on Add and enter the details of the client device
- Select the devices to enable access and click allow.
- Apply the settings.
5. Configure a VPN

A VPN encrypts all the internet traffic routed via the wireless router. This will make it difficult for any attacker to eavesdrop on your wireless communication.
Configuring a VPN on your router will help you keep any work-related data confidential when you are working from your home.
Steps to Configure a VPN:
- Login to the router's admin
- Navigate to advanced setup
- Click on the VPN service
- Check the VPN service check box
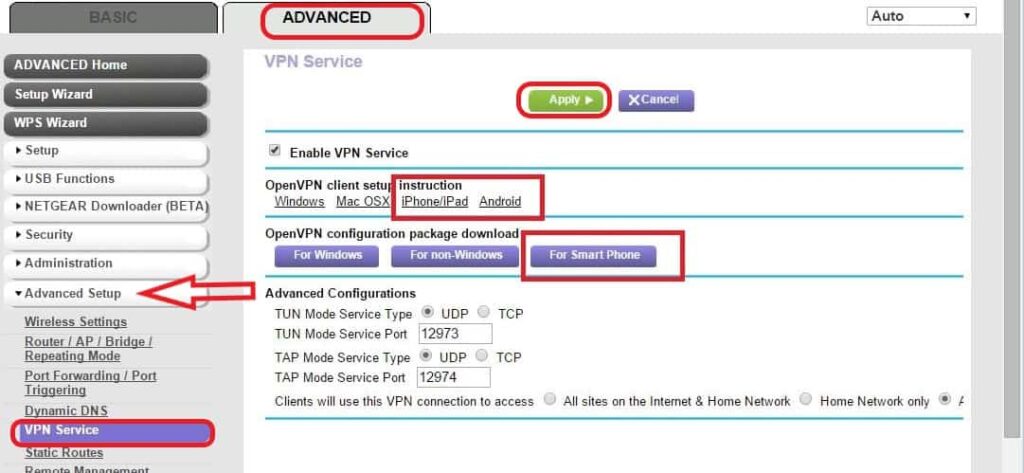
- You can download and install the VPN package on the devices if you want protection while using any public WiFi service.
- Click on Apply and save the settings.
6. Disable UPnP
UPnP enables apps and devices like gaming consoles, smart TV, IoT gadgets, and security camera to share the LAN network to communicate with each other conveniently.
This makes it vulnerable to attack by potentially allowing unauthorized devices to gain access to the network. Disabling the UPnP feature in the router will reduce the potential of an attack.
Steps to Disable UPnP:
- In the router's admin page, Navigate to the advanced settings tab
- Click on the Advanced Setup menu
- Choose UPnP
- Uncheck the Turn UPnP ON
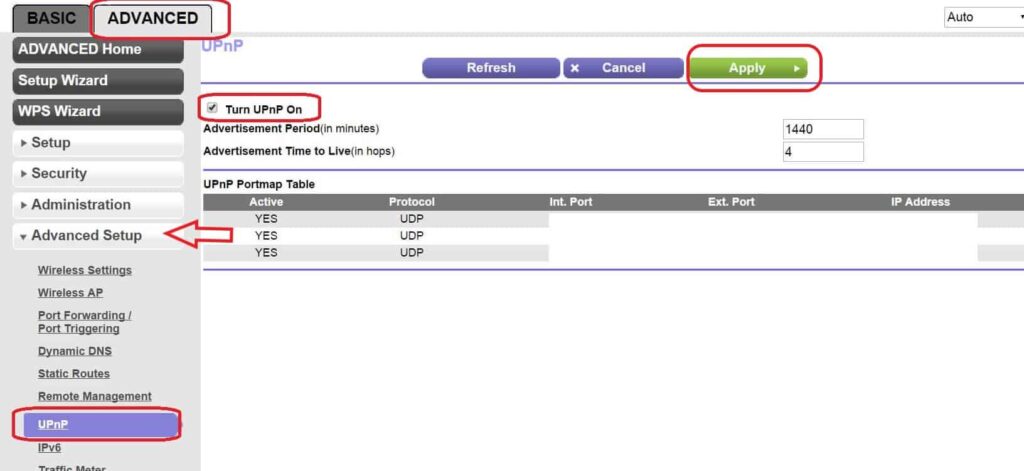
- Click on Apply and save the settings
7. Keep Your Router Up To Date
Your router receives frequent updates to its firmware from its manufacturer. This will include operational efficiency, features, and security fixes.
Keeping the router on the latest version of firmware will keep your network safe from potential attacks rising out of the vulnerability in the previous version of the firmware.
Steps to update your firmware
- Go to OEM’s official support page
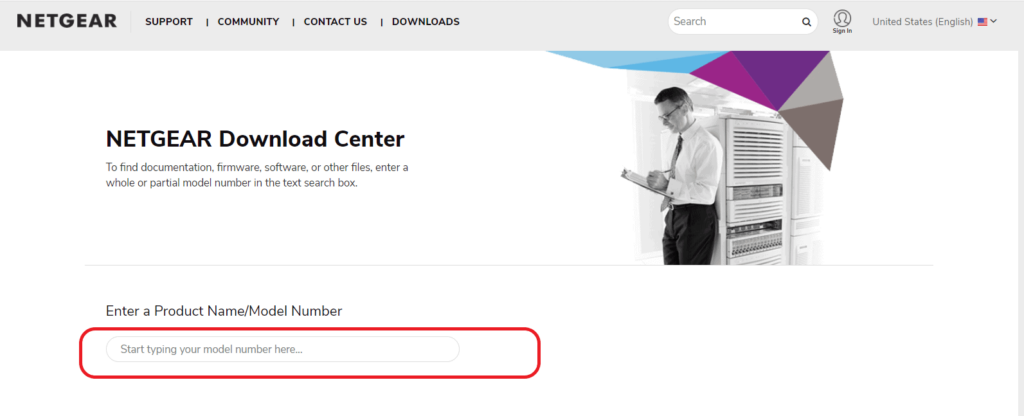
- Search for your router model
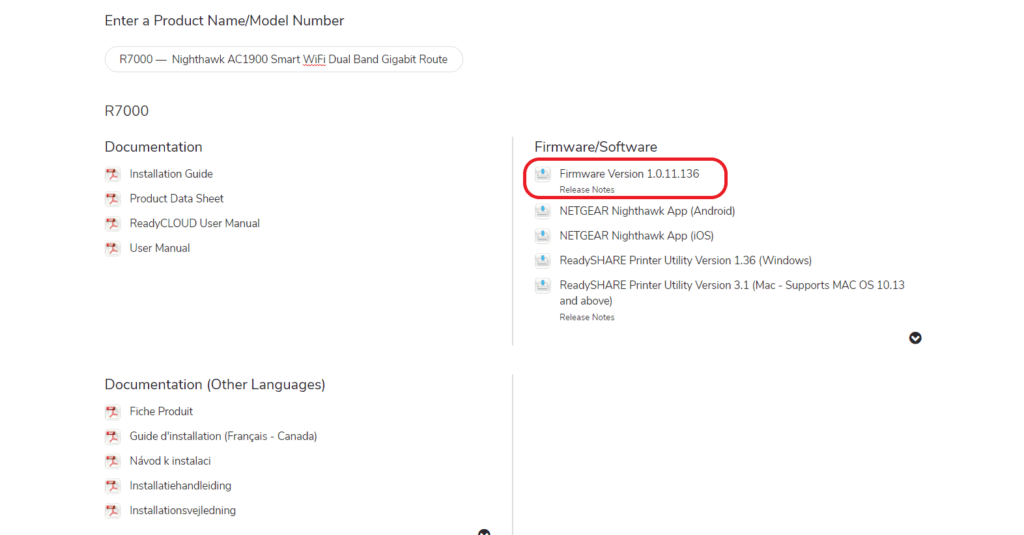
- Download the latest firmware version
- Login to the admin portal
- Go to the Advanced settings and click on Administration settings
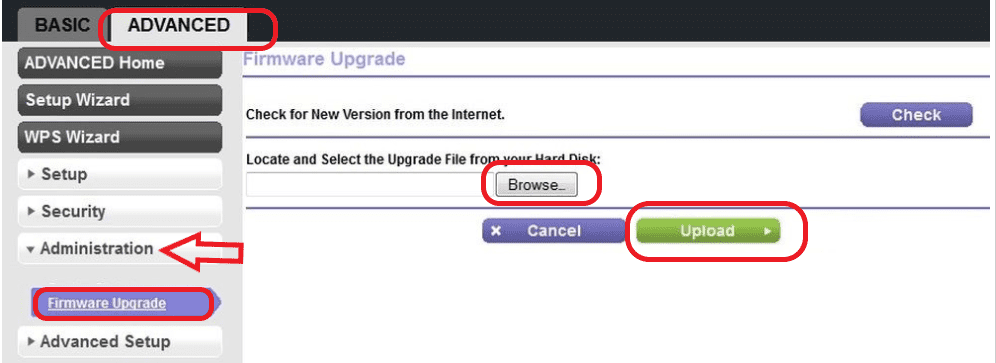
- Click on firmware upgrade
- Browse and map the downloaded firmware file
- Click on Upload
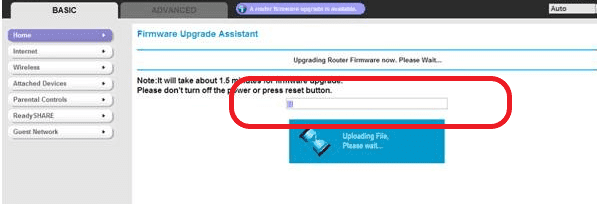
- Wait until the upload and installation are complete.
8. Check for Unauthorized Wi-Fi Access
Do a routine check on your home network for the list of devices connected to the network. If the list of devices accessing your network has any unauthorized devices, you can block them. This will help you avoid any piggybacking or loss of bandwidth.
Steps to Block Un-authorized Wi-Fi Devices:
- Login to the admin portal
- Click on the attached devices to find the list of devices that access your wireless networks
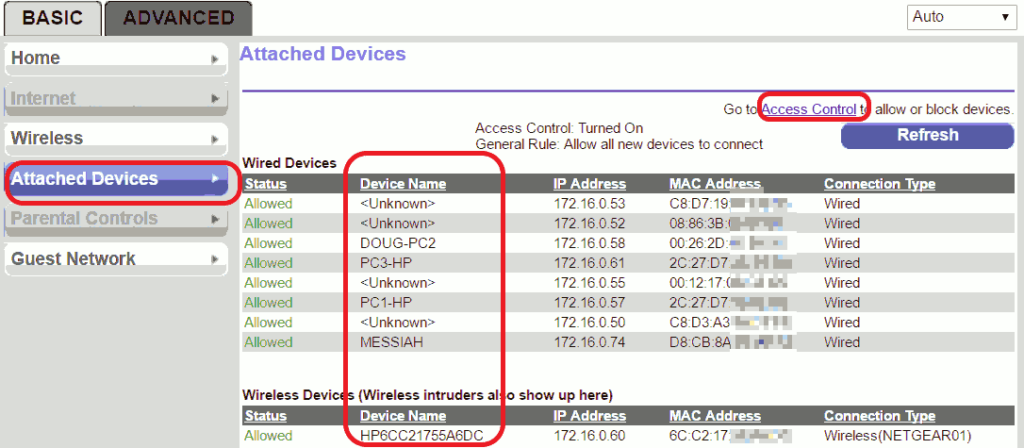
- Once you spotted the devices, go to access control in the advanced security tab
- Select the devices and click the block. Apply the settings.
9. Disable Unnecessary Optimization
One of the best ways to protect wireless networks is to disable any unnecessary service, settings, or customization.
While these services have a legitimate purpose, if you are not aware of their usage leaving them enabled opens the possibility to launch DoS and other attacks. This includes services like remote management, USB settings or FTP, and HTTP.
Steps to Disable HTTP/FTP:
- Login to the admin portal
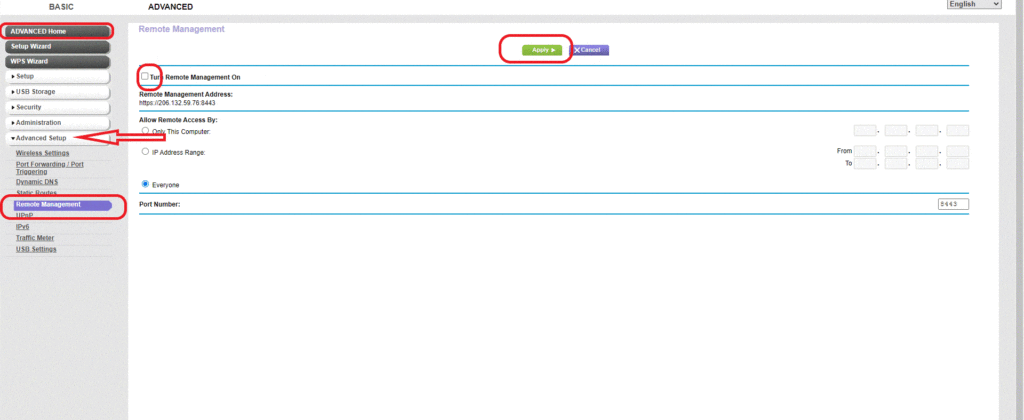
- Go to the advanced settings tab
- Click on the advanced setup
- Select remote management and uncheck the box as highlighted
- Click Apply and save the settings.
- In the Advance setup menu, Click on port forwarding
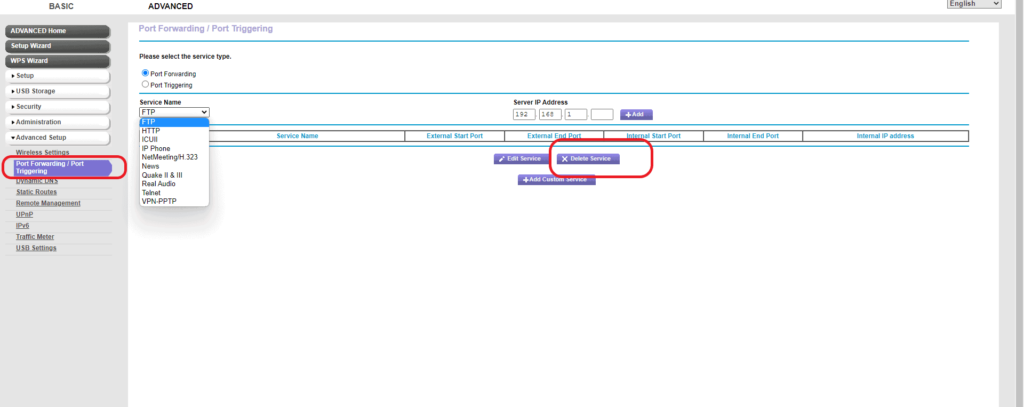
- In the dropdown, click on the service name and look for any services running.
- Choose the service and click delete.
Note: If you're a customization freak, I'd rather suggest you get either of the following third-party firmware routers:
Frequently Asked Questions
Using strong passwords, encryption, and VPN service is among the best security for wireless networks that will allow you to protect the information while wireless communication.
WPA 3 is the latest encryption technology to protect your wireless network.
Wardriving, traffic monitoring, DoS attacks, Spoofing, session hijacking, rogue access points, and evil twin attack are some of the threats to network security.
Conclusion
Following the home network security practices explained in the article above, one can avoid the most imminent threats to a wireless home network. While these practices can protect you from the external test, using your devices in public WiFi might compromise their security.
Using a VPN service and antivirus software installed in the device will help you keep the device safe and keep your home network safe from the possibility of a potential attack.





