If you are a networking enthusiast who wants to learn the differences between WiFi 6, 6E, and the much-hyped latest Wi-Fi 7, you are in the right place. Let's compare all three wireless standards and know how they differ & translate to performance in real life.
The major features of Wi-Fi 6 and 6E are the same, except for the additional 6 GHz band in 6E, which helps easily navigate congested networks. While the next-generation Wi-Fi 7 doubles the bandwidth and triples the throughput capacity.
Credit to its far superior amplitude modulation and double the number of spatial streams, Wi-Fi 7 will take your wireless experience on par with wired ones. How? Let's find out!
WiFi 6 vs 6E vs 7: Technical Differences
| Aspect | Wi-Fi 6 | Wi-Fi 6E | Wi-Fi 7 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IEEE Standard | 802.11ax | 802.11ax | 802.11be |
| Speed Capacity | 9.6 Gbps | 9.6 Gbps | 46 Gbps |
| Frequency Bands | 2.4GHz and 5GHz | 2.4GHz, 5GHz, 6GHz | 2.4GHz, 5GHz, 6GHz |
| QAM Modulation | 1024-QAM | 1024-QAM | 4096-QAM |
| Channel Width | 160 MHz | 160 MHz | 320 MHz |
| Access Point | Single | Single | Multiple |
| Spatial Streams | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| WiFi Security | WPA 3 | WPA 3 | WPA 4 (TBD) |
Briefing WiFi 6, 6E, and WiFi 7
What Is WiFi 6?
Wi-Fi 6, announced in the year 2019, made huge improvements by introducing ODFMA, improvements to power consumption, and bi-directional MU-MIMO. Operating in both 2.4 and 5 GHz frequencies, the efficiency saw a sizeable throughput increase of over 30% from the previous generation.
Suggested Read: Throughput vs Latency
What Is WiFi 6E?
As an extension of Wi-Fi 6, 6E was announced a year later in 2020, extending all the features into a third band, 6 GHz.
Features like OFDMA, target wake time, and low latency operating in three simultaneous bands became a significant advantage in improving throughout per square-feet area, particularly in highly congested environments.
With the launch of the 6E wireless standard, networking companies implemented the 6GHz band networking devices. You can find my top picks here:
What Is WiFi 7?
WiFi 7 will release with huge amendments in progress since its initial draft in 2021. The 802.11be, aka WiFi 7, doubles bandwidth with 320Hz channels.
With the QAM quadrupled, and spatial streams increased, the speed throughputs are pitted at 30 Gbps while operating in all three bands 2.4, 5, and 6 GHz.
WiFi 6 vs WiFi 6E vs WiFi 7: Detailed Comparison
In this section, I’ll compare WiFi 6 and 6E with WiFi 7 in several important factors.
Speeds & Suitability
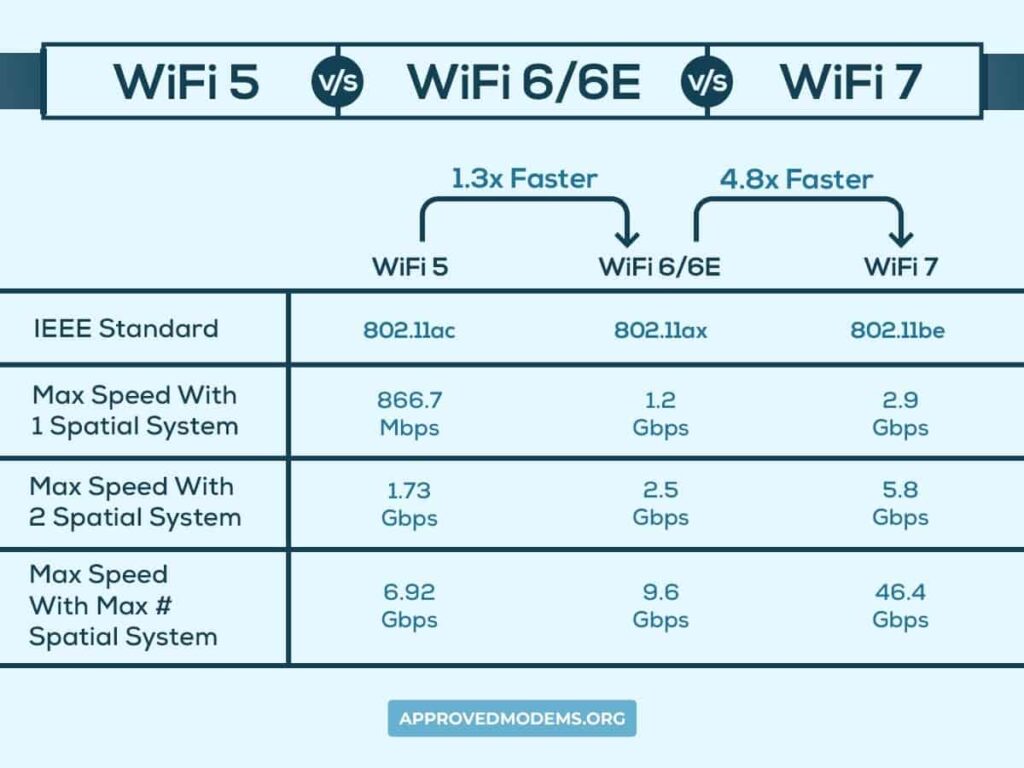
While comparing WiFi 6 vs 6E in terms of speed capabilities, they seem to deliver a throughput capacity of 9.6 Gbps, which was a huge jump from the speeds offered by the Wi-Fi 5 standard, which was capped at 6.9 Gbps.
To take advantage of the efficiency of the 6th generation of wireless standards, you'll need the OEMs incorporating them in the latest client devices like smartphones, tablets, gaming consoles, etc.
The impending announcement of the WiFi 7 standard triples the theoretical speed capacities up to 30 Gbps. The WiFi 7 speed will demand a new set of manufacturing standards with highly capable gadgets and IoT devices designed to operate in multiple frequencies.
Frequency Bands
Wi-Fi 6 operates in two major frequencies, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Both these frequencies have been getting congested with the increase of wireless devices.
Wi-Fi 6E extends all the operational efficiency to an additional 6 GHz band to circumvent network interference and congestion issues.
Including the 6 GHz bands will improve the speeds achieved in the shorter range. WiFi 7 operates on all three frequency bands, 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz & 6 GHz, similar to 6E, combined with improved efficiency in other aspects.
This will allow next-generation WiFi technology to accommodate more gadgets and better performance in an area.
Channel Width
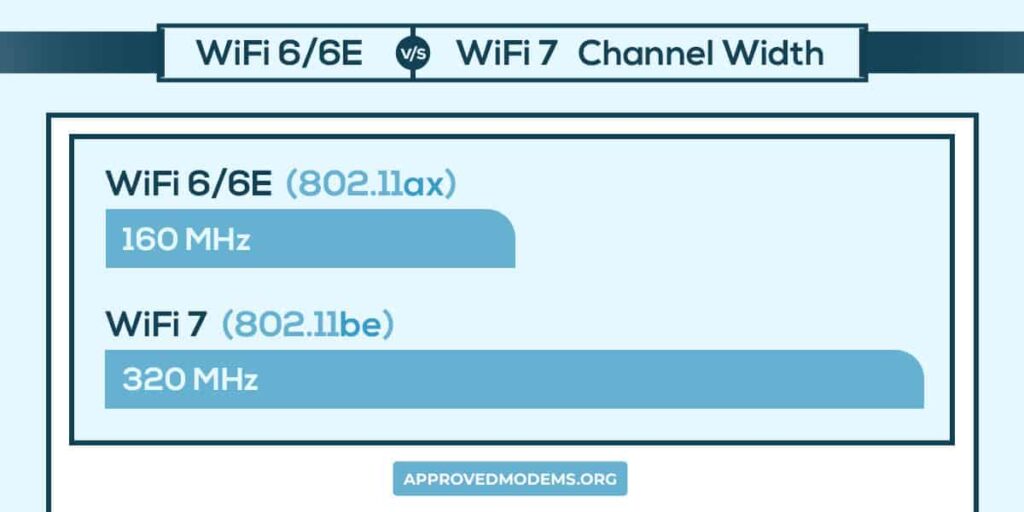
While the second wave of 802.11ac witnessed the usage of a wider 80 MHz channels, the huge jumps throughout were achieved by introducing 160 MHz channels in the WiFi 6 routers.
The extended version of Wi-Fi 6E is reaping the benefits of wider 160 MHz channels to its full extent, which has led to higher throughputs in WiFi 6E routers.
With the WiFi 7 release date on the horizon, there are further improvements. The newer generation of wireless devices will exploit even wider 320 MHz channels, opening up superior efficiency and throughput levels.
QAM Modulation
QAM modulation decides how data is packed and transmitted over the radio frequencies. The denser the modulation, the higher the amount of data that can be transmitted without hassle. The rise of high-quality 4K streaming and AR/VR content tested the limits of Wi-Fi 5, which was operating at 256-QAM.
Wi-Fi 6 and 6E came up with a higher modulation, operating at 1024-QAM. Wi-Fi 7 takes it even further and brings a lot of efficiency with an even denser modulation at 4096-QAM. This effectively reflects throughput speeds and makes higher speeds, like 30 Gbps, conceivable.
Data Streams
The 6th generation of Wireless standards brought bidirectional MU-MIMO into practical usage and doubled the number of spatial streams to 8 over the Wi-Fi 5's 4×4 MU-MIMO. This would allow up to 8 simultaneous connections to access the internet without losing the speed throughput.
Wi-Fi 6 and 6E employ bi-directional 8 x 8 MU-MIMO. WiFi 7 increases the number of spatial streams to 16. This will allow up to 16 devices to crank up data at high speeds.
The next generation of IoT gadgets will exploit this efficiency brought in by the latest wireless technology.
Access Points
In Wi-Fi 6 and 6E, the client devices can use only one frequency band at a time, i.e 2.4/5/6 GHz. The smart connect feature allows devices to switch between these bands automatically, depending on signal quality and interference.
With Wi-Fi 7, it's a whole new game. Introducing MLO (Multi-Link Operation) allows the client devices to send and receive data across different bands and channels. This will reduce the latency in communication to a bare minimum. This allows you a wireless experience akin to wired internet.
A significant improvement in reliability while using AR applications and online gaming.
WiFi Security
WiFi 6 and 6E witnessed a superior security encryption standard WPA 3 which uses protected management frames and a 4-way handshake authentication protocol to keep your connections secure from any offline attacks in which WPA2 was vulnerable.
We are not expecting WiFi 7 routers for another year. But when they arrive in the market, they might show up with even superior WPA4 encryption standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
The speeds offered by Wi-Fi 6 standards are adequate for an excellent gaming experience. But if you are switching to VR/AR-based games, the additional 6 GHz band will be valuable to a reliable gaming experience.
The Wi-Fi 6E offers an additional band with the other advantages that come with the standards of 6. This gives it a tremendous advantage in circumventing network congestion and interference.
Indirectly, Yes. The performance efficiency of Wi-Fi 7 will directly impact the signal quality. The additional band, wider channels, and double the number of spatial streams will cause better performance at a distance.
Although the touted theoretical speeds are rated as high as 30 Gbps, achieving those speeds in a practical environment will be challenging. However, the internet throughput for individual client devices is expected to be around close 5Gbps, more than double the speeds achieved in Wi-Fi 6 standards.
Conclusion
A router with Wi-Fi 6 standards will be sufficient for an average home user. Most of the client devices in usage are majority Wi-Fi 5, which will remain relevant for the foreseeable future. It makes more sense to choose 6E if you are in a smart home and running a household with over 40 devices.
The WiFi 7 speed is well above what's available to a home user, making it overkill. It would be a better fit for commercial spaces and medium-sized offices.





