Are you experiencing weaker signals and network dead zones in your house but confused as to which option to go with, WiFi mesh or extender?
While both types of devices are meant to expand WiFi coverage, they differ in terms of functionality, performance, and of course, price. Let's dig deep into the differences between WiFi mesh and Extender.
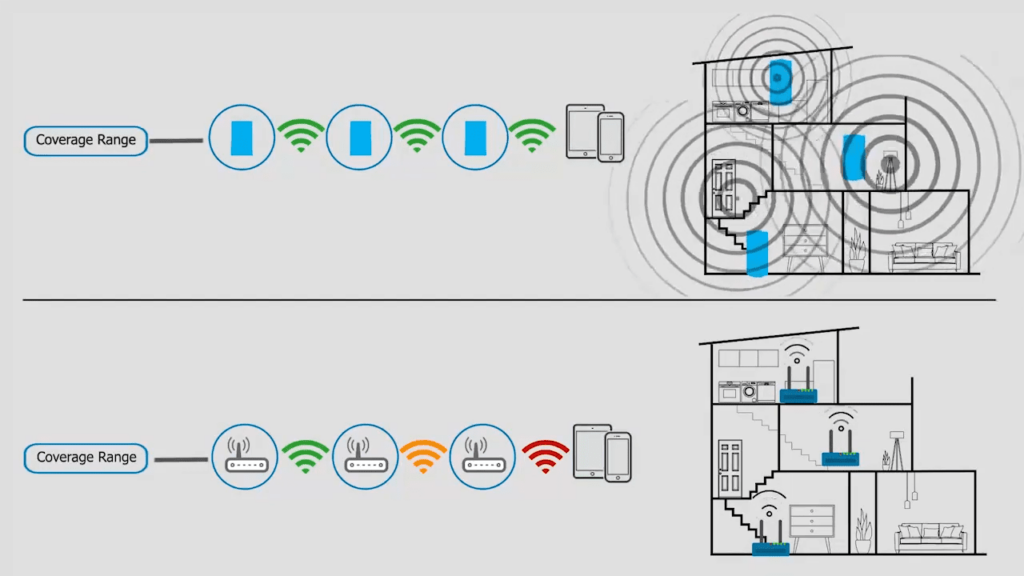
As shown in the picture above, WiFi mesh travel signals from the router to multiple nodes placed at different locations in a house and works as extensions to expand the coverage. While the range extender repeats its signals from a router.
Key Takeaway: Mesh WiFi systems offer seamless connectivity and are way better than extenders in most aspects, including speed, coverage range, signal quality, and reliability. However, they're pricey.
WiFi Mesh vs Extender: Detailed Comparison
To establish a clear picture, I’ve compared the two in several aspects. Going through the subsequent sections should give you an idea as to what suits you the best.
Furthermore, both overpower the other in certain aspects, so the final decision will rest upon your requirements. So without further ado, let’s get started!
Functionality
Let’s start by explaining how WiFi extenders work. These are separate devices placed just between your “network dead zones” and router, to which it’s hooked up wirelessly or through a wire.
Extenders grab the signals sent by the router and broadcast them to another channel, relaying the connection to the spot you want to be covered.
In simplistic terms, a WiFi extender acts as a middleman between your router and the dead zone, extending the former signals to the rest of the home.
So, you can access the internet signals anywhere, no matter the obstruction. But ensure that the extender is close enough to the router to receive signals and far enough to rebroadcast the signals to the dead zones.
On the other hand, here's how mesh networks work: Mesh WiFi contains multiple units including a main router and others acting as nodes or satellites.
So the main unit connects to the satellites placed around the house wirelessly or through an Ethernet cable and gets access to the signals which are further transmitted to the client devices.
In this manner, a mesh network is created around the house, and users get the best signals anywhere they go.
Coverage & Signal Quality
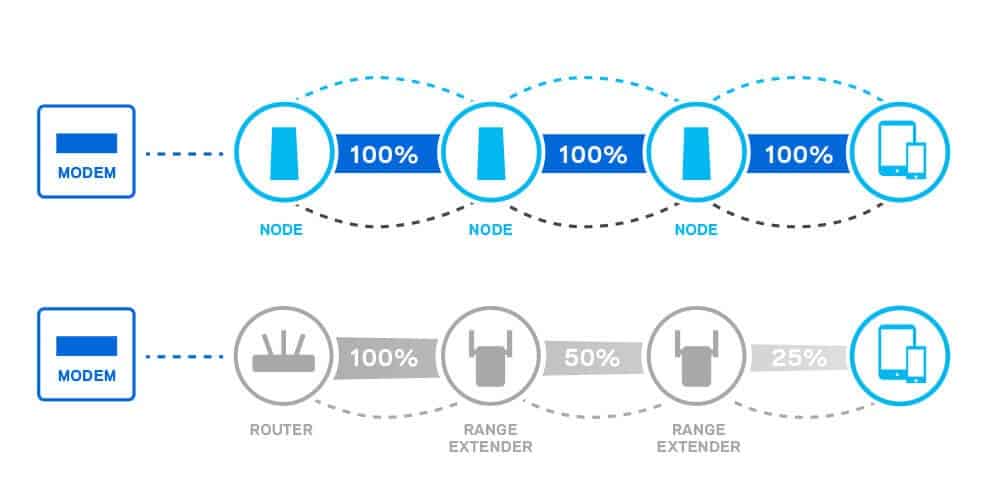
From the functionality, it can be deduced that WiFi extenders create an additional channel to rebroadcast the signals to your smart and wireless home devices to use.
For example: if the network SSID for the router is ElenaWiFi, for extenders, it would be ElenaWiFi_EXT.
They aren’t capable of broadcasting signals at the maximum strength they’re capable of, regardless of the incoming signal strength.
This is not the case with mesh WiFi. The satellites that come along share similar capabilities to the main hub, and therefore signals of almost equal strength are broadcasted around the house.
P.S: Signals do lose their strength by a tad when are rebroadcasted from one device to another, but it doesn’t majorly affect the performance.
WiFi Speeds
Now, the maximum speeds your devices can attain depends on the quality of signals they receive. This is where the speeds take a hit when signals are broadcasted from the extenders. But you shouldn’t expect major speed drops when connected to mesh WiFi.
For example, I had TP-Link RE550 connected to the same router, i.e., ASUS RT-AX86U, and measured respective speeds with an Xfinity Gigabit plan, and the download speed was around 210 Mbps.
Similarly, with TP-Link Deco X55, the respective speed value clocked at 567 Mbps, much of an upgrade to the extenders.
Price to Value
When it comes to price, mesh WiFi costs much higher compared to extenders, possibly three to four times.
So, if you have a router pre-installed and don’t have the facilities to upgrade to a mesh system, yet eliminate the network dead zones, extenders should do the job for you.
Besides, there are a few extenders with mesh tech that delivers slightly better performance, so you can opt for them as well. But, with these, the compatibility factor comes into the picture, verify that before purchasing one.
Mesh WiFi, on the other hand, gives you every single worth of your money by delivering exceptional coverage, almost equivalent speeds throughout, and establishing connections on multiple devices at once. So, make your choice wisely.
Ease of Setup
Both the setups draw in this department, despite involving a different process.
The only issue with the extenders is their placement, i.e., where to place an extender, as a few inches here and there would result in a weak connection in the extremities.
So, as soon as you get the perfect spot, connect to the router wired or wirelessly by pressing the WPS switch on the top. Wait for it to turn green. Once it does, log in to the ISP website, then find and click the “add extender” option.
Note: If both devices support WPS connectivity, you can also connect the WiFi extender to a router using WPS.
Moving on to the mesh WiFi, most have a compatible app that entails detailed instructions making it much easier for users to get it installed within a few seconds.
Besides, they update their firmware automatically, which is a struggle for extenders, where you must check the manufacturer’s web page for updates, and download a file manually.
Reliability & Scalability
Whether mesh or WiFi extender, both are reliable in their own way, provided you add a decent device to the setup. Both serve the purpose of extending your signals far away, but if you are concerned about signal strength and speed, mesh systems are synonymous with reliability.
Mesh systems are more scalable than WiFi extenders as you can add multiple satellites to the setup and expand the coverage, depending on your needs, which isn’t the case with extenders.
Advantages & Disadvantages of a Mesh WiFi
Pros
- If one node is weak, devices will automatically switch to other
- Easy to set up & manage
- Highly scalable
- Can handle multiple devices with ease
Cons
- Require strong broadband speeds
- Can be a costly endeavor
Advantages & Disadvantages of a WiFi Extender
Pros
- Overcomes obstructions
- Transmits signals to a longer distance
- A cheaper solution to get rid of dead spots
- Easy to install
Cons
- Cuts down the speeds
- Requires you to select the optimal spot
Can You Use a WiFi Extender with a Mesh Network?
Yes, you can add a WiFi extender to the mesh network, but it won’t work like a mesh node, and rather just range extenders. It will just expand the signal coverage but you won’t have access to the seamless roaming support.
Key Takeaways
- Range extenders typically just retransmit the signals they receive from the routers using a different channel, which results in slow WiFi in multiple areas.
- And with the use of the same channel, signals travel from node to node, and the same is not the case with mesh extenders.
- Mesh extenders have a compatible app that makes their installation much simpler, besides coming with a range of features to let you manage it without ruffling any feathers.
- Mesh systems are much costlier than extenders, and are more scalable as well as reliable than the latter.
Note: If you've decided on the type of device you need, it's important that you select the right model. Only then you'd be able to make the most of your network. If you're unsure, you may check my recommendations for both types of devices here:
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, with the way Mesh WiFi performs, you stay connected to the best possible network every time, thanks to its seamless roaming tech. Besides, it’s capable of delivering strong signals to many devices at a time, without cutting down the signal strength. It’s definitely the better option, provided you have the budget for that.
Although you can you shouldn’t connect two-three WiFi extenders at the same time. They interfere with each other if there aren’t any separate channels for each.
Network extenders usually work on a separate channel and it appears as a different name, for example, “NetworkName_EXT”, while there is a single network name for mesh routers.
WiFi extenders are the cheapest devices that expand the range of your router by around a thousand or more square feet. Although there’s a speed drop in the extended range, it’s worth an investment.
If you go by the features and in turn overall performance, mesh WiFi is the best among the rest. But at 3-4 times less the price, extenders do a decent enough job for you, provided you get a decent enough device.
Conclusion
With that, comes an end to the mesh WiFi vs extender guide. As I have mentioned many times here, mesh WiFi stays miles ahead of extenders in terms of performance, but also in cost. So if your only purpose is to transmit signals to large spaces and isn’t concerned much about the speeds, then an extender is the best you’ve got.





