2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz: What Should You Use in 2025?

The 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz refer to the two different radio frequencies currently used by most wireless routers to broadcast WiFi connections.
Key Takeaway:
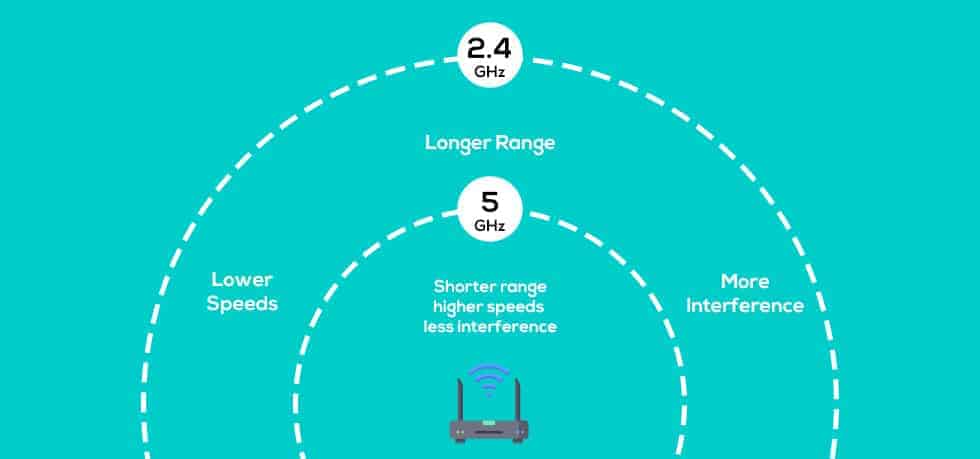
The major difference between 2.4 and 5 GHz is that the latter offers faster speeds. On the other hand, the 2.4 GHz offers a much better range but comes at the cost of a slower speed.
But there’s much more to the 2.4 vs 5 GHz comparison than range and speed. You should know more about these bands before selecting which one to use for your home network. Continue reading to learn more about each frequency band and how to choose one.
2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz: The Key Differences
What is 2.4 GHz WiFi?
The 2.4 GHz frequency provides a large coverage area as well as being better at boosting WiFi signals through walls, with a usable speed of up to 300-450 Mpps (depending on the model of your router). On the other hand, its data range is smaller and very susceptible to interference and congestion.
What is 5 GHz WiFi?
The 5 GHz frequency provides the users with a wider data range with minimal interference and provides a fantastic bid for broadband internet for WiFi at home, reaching up to 1300 Mbps speed. Contrary to this advantage, it has a limited coverage area and is ineffective at penetrating walls and solid objects.
2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz: Detailed Comparison
Now that I’ve briefed both frequency bands, it’s time to compare 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz on various factors to find out which one is better in what aspects and why.
1. Speeds & Throughput
The maximum WiFi speed does not always depend on a wireless device’s GHz range. What should be taken into account most is the WiFi router’s placement.
For example, the 2.4 GHz band typically supports up to 300 Mbps or 450 Mbps, depending on the router model; however, because so many devices use the 2.4 GHz band, congestion can result in less stability and slower internet speeds.
The 5 GHz band, on the other hand, can offer high speeds of up to 1300 Mbps. It is less congested than the 2.4 GHz band since very few devices use it, and it offers more WiFi channels for your devices to use than the 2.4 GHz band.
The maximum speed would be determined by the wireless standard supported by the access point, which could be 802.11n, 802.11g, 802.11b, or 802.11ac.
The 5GHz band offers significantly faster speeds when compared to the 2.4GHz band. Simply put, the 5GHz band can carry more data and transmit it faster. The 5GHz band should be your choice if your top priority is to deliver a great WiFi speed performance.
2. WiFi Coverage
WiFi coverage refers to how far a wireless router’s signal can travel while still effectively connecting to other devices. Since it can pass through solid objects, 2.4 GHz typically has a wider reach than 5 GHz.
Due to its extremely high frequency, 5GHz cannot penetrate through obstacles. These are some typical examples of these obstacles:
- Concrete walls
- Floors and Ceilings
- Big furniture
While difficult to penetrate at 5GHz, these items are easily penetrated by 2.4GHz transmissions. The 2.4 GHz band is the best option if your WiFi network needs to reach a larger area or one surrounded by walls or other solid objects.
Many common WiFi routers that use the 2.4 GHz frequency band can transmit signals up to 150 feet (46 meters) inside and 300 feet (92 meters) outside without taking any other external forces or significant obstructions into account.
For instance, the 2.4 GHz band will be suitable for multi-level buildings, big houses, and large retail stores.
The 5 GHz, on the other hand, frequency has a reach of roughly one-third of the above-mentioned distances and is most suitable for locations without physical obstructions due to its shorter effective range.
Talking about coverage distance, you can expect good signal strength up to 50 feet (15 meters) inside the house. This type of band would suit small homes or apartments.
3. Network Interference
Another thing to look out for is possible interference with the band of the WiFi network. A network can be significantly slowed down by interference, which also narrows the network’s application.
For example, mobile phones and microwave ovens are the two most common causes of network interference in the 2.4GHz band. On the other hand, the most common sources of network interference for the 5GHz frequency are smartphones, radar systems, perimeter sensors, and digital satellites.
It is common for interference to occur when multiple devices use the same frequency, which can impact signal strength and slow down upload speed. The interference from other devices may also cause your wireless connection on a specific frequency band to be faster or slower.
The 2.4GHz band’s waves are better suitable for longer distances and transmission through solid objects like walls. Because of this, 2.4GHz is more practical if you live in a densely packed area or have a lot of walls or other solid objects between your device and router.
On the other hand, the shorter waves of the 5GHz band make it less efficient at passing through walls and other solid objects. This occurs as a result of the peculiar properties of electromagnetic waves, which are stronger at higher frequencies (5GHz).
And hence, multiple obstacles such as walls, floors, ceilings, doors, and others can easily impact the signal.
In general, 2.4 GHz WiFi connections are subject to more interference from neighboring devices than 5 GHz WiFi connections. As a result, your connection will slow down if your WiFi network is near a lot of interference from other devices or appliances. And that is why I advise shifting your devices to the newer 5 GHz WiFi network.
However, if you want better signal coverage at your place, using the 2.4 GHz network would be a wiser decision.
4. Channels & Wavelength
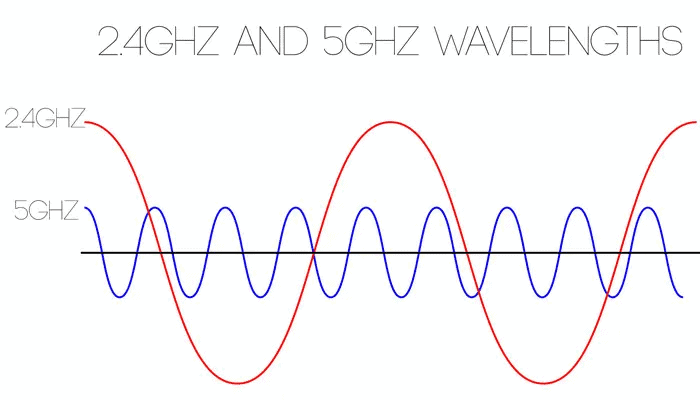
Your connection won’t always be faster if you increase the channel width. A larger channel means a higher data rate.
Simply put, more data can be sent per second using your signal. However, if your internet speed is too slow, like 1 Mbps, 3 Mbps, or 5 Mbps, having a wider channel will not help or improve anything.
Even if you have a lightning-fast internet connection, you must take caution when using a wider channel. It can cause more interference and slow down your connection.
Your router can transmit signals in the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands on various channels. There are 14 channels at 2.4 GHz. However, there are only three non-overlapping channels.
5 GHz, on the other hand, has 24 channels, none of which overlap. Your router can use these frequency ranges to optimize your connection by bringing down interference.
How To Choose Between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz?
1. The Size of Your House
Bigger houses will necessitate a larger coverage area, and hence the 2.4 GHz frequency band is ideal for this.
On the other hand, if you live in a small house, 5 GHz would be a much better option. It will not only offer improved WiFi speed but will also be safer from network interference from your neighboring houses.
That being said, it’s necessary to consider WiFi extenders and mesh systems for large homes, which allow you to expand your WiFi network coverage while taking advantage of all the benefits of the 5GHz band.
2. Interferences and Congestion
Since so many devices use the 2.4GHz band, it is more susceptible to interference and congestion. And by saying so many devices, I mean other routers, smartphones, Bluetooth devices like earbuds, microwave ovens, and more.
This is where the 5 GHz band shines, as it’s less susceptible to interference and congestion. So if you live in a densely packed area, a 5 GHz band will offer you great connectivity and stability by avoiding such inferences, considering that you are close to the router.
Fewer overlap results in less interference, which leads to improved performance.
Additional Note: With the launch of Wi-Fi 6E, you get a new 6 GHz band with even less congestion. I’ve discussed it in detail in my Wi-Fi 6 vs 6E vs Wi-Fi 7 comparison.
3. Device Type and Usage
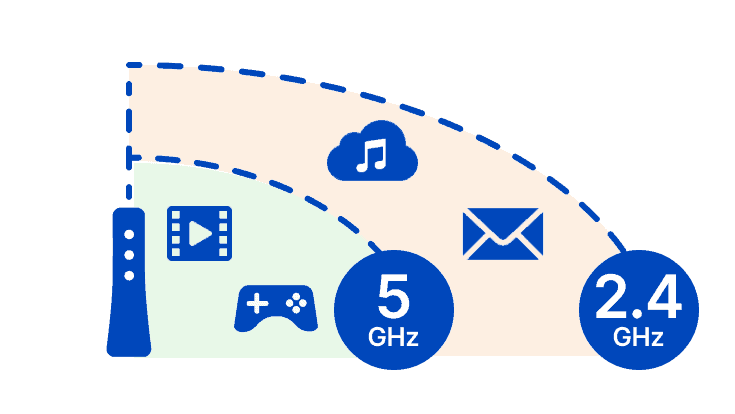
Because the 2.4GHz band employs longer waves, it is usually preferred for longer distances or transmitting through solid objects and walls.
Generally speaking, you should connect phones and other devices to the 2.4GHz band for low-bandwidth tasks like surfing the Internet. 5GHz, on the other hand, is best designed for high-bandwidth tasks such as gaming and streaming HD content.
The goal is to allocate your devices across both bands, so there is less contest for the same data range. Keeping your Internet of Things (IoT) and personal devices separate can improve WiFi security.
You can optimize your network’s performance by distributing your devices between 2.4 and 5 GHz.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which is better 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz?
It depends on different factors. If you live in a small house and need fast internet speed, a 5 GHz band is a better option. While a 2.4 GHz band would do the job if you reside in a big house and don’t do activities that require high bandwidth.
What devices should be on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz?
You should connect those devices to a 2.4 GHz network which requires less bandwidth and are used even at the corners of the house, like phones, work laptops, smart speakers, and other smart home devices. 5 GHz should be allocated to devices that require more bandwidth, like gaming pc and Smart TVs for streaming content.
Can I use both 2.4 and 5GHz at the same time?
Yes, if you have a dual-band router that supports both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Note that you can only connect one device to a single band at a time. To connect to both bands, you would need two or more devices.
How to change from 2.4 GHz to 5 GHz?
If your router supports the 5 GHz band, simply go to the browser and sign in to your router settings aka admin panel. Then go to the connection/wireless menu and click on enable under 5 GHz Wireless. Don’t forget to apply the settings before exiting.
Conclusion
So, that was everything about my 5 GHz vs 2.4 GHz comparison. If you are still confused about whether to choose 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, I advise setting it in auto mode. A router that uses both bands is the perfect combination of both worlds.
